A Further Look at Material Deprivation
Chart 1

In the South Caucasus as a whole, people who list salaries as their household’s primary source of income have half the average material deprivation rate of 32%. By taking the ratio of the average rate of material deprivation (blue bar) and the material deprivation rate for salaries as the primary source of income (red bar), Chart 2 shows that households primarily relying on salaries for income have less than half (44%) the average material deprivation rate in Armenia. This figure is 52% of the average material deprivation rate in Georgia, and 63% of the average material deprivation rate in Azerbaijan. Furthermore, households in the South Caucasus that did not report salaries as an income source are 1.4 times as likely to be materially deprived.
Chart 2

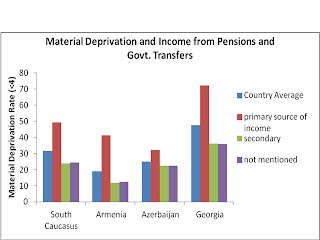
Pensions and government transfers are the second most important source of income in the South Caucasus. Chart 3 shows that households where government transfers are the primary source of income have more than 1.5 times the average rate of material deprivation, while those where pensions and government transfers are the second source of income have three-fourths the average rate of material deprivation. This suggests that government transfers throughout the South Caucasus are not large enough to live without poverty, but can effectively supplement a main income. The trend is most extreme in Armenia where households relying on the government for their primary source of income are over two times as likely to be materially deprived, while households where government funds are a secondary source of income have three-fifths the average rate of material deprivation. In Azerbaijan, government transfers have a much weaker correlation with material deprivation. In fact, data from graphs 2 and 3 shows that households receiving government transfers as their primary source of income are twice as likely to be materially deprived as households dependent on salaries in Azerbaijan, three times as likely in Georgia, and five times as likely in Armenia.
Chart 3
As chart 4 shows, income from sales of agricultural products is correlated with higher material deprivation rates across the South Caucasus, supporting previous findings showing that material deprivation is concentrated in rural areas. Armenia has the lowest percentage of households reporting income from the sale of agricultural goods, and also the smallest changes in material deprivation based on income from agriculture. Georgian households dependent on agriculture for either their primary or secondary source of funding are around 1.4 times more likely to be materially deprived than the country average, while Azerbaijani households are almost 1.8 times as likely. In Armenia and Georgia, relying on pensions and government transfers is the strongest indicator of material deprivation, while in Azerbaijan it is dependence on sales from agricultural products.
Chart 4

Only 13% of respondents in the South Caucasus report receiving money from remittances, but chart 5 shows that households most reliant on remittances are less likely to be materially deprived. The trend is especially strong in Georgia, where households dependent on remittances as the primary source of income have 58% of the country’s average material deprivation rate.

Although overall trends are consistent across all three South Caucasus countries, the importance of each income source on standard of living varies rather widely. Material deprivation in Azerbaijan seems to reflect a large divide between urban and rural areas, with family transfers, salaries, and government transfers much less strongly correlated to changes in material deprivation than in Georgia or Armenia. In Georgia more people mention government transfers than salaries as an income source, and for those reliant on state transfers, the material deprivation rate is over 70%. Although Armenia has by far the lowest material deprivation rate, at under 19%, it has a huge disparity between households with salaries as their primary source of income and households dependent on government transfers.
An interesting implication of the 2014 census: Georgia is likely an upper middle income country
Trust in institutions in the South Caucasus – generating a combined score
სოციალური და პოლიტიკური ინსტიტუტების მიმართ ნდობის ცვლილება საქართველოში
მოსახლეობის ნდობის დონეს მთავრობისა და სხვა ინსტიტუტების მიმართ ბევრი ფაქტორი განაპირობებს. ამ ფაქტორების გავლენით დროთა განმავლობაში ნდობა შეიძლება, შეიცვალოს. CRRC-საქართველოს მიერ 2011-2015 წლებში ჩატარებული კავკასიის ბარომეტრის და NDI-ის საზოგადოებრივი აზრის გამოკითხვების შედეგებზე დაყრდნობით ამ ბლოგში აღწერილია ბოლო წლებში ნდობის დონის ცვლილება პრეზიდენტის, ადგილობრივი მთავრობის, აღმასრულებელი ხელისუფლების, პარლამენტის, ჯარის, ჯანდაცვის სისტემის, პოლიციის, განათლების სისტემისა და სასამრთლოს მიმართ.Income Levels in Georgia from 2008 to 2013
Georgia—Abkhazia
The Olympics in Sochi, Russia, took place about 30 kilometers from Russia’s border with the separatist region of Abkhazia in Georgia. As a security precaution, the Russian government has temporarily moved its border 11 kilometers into Abkhazia to create a “security zone,” at which travelers entering will have to show identification before proceeding to the actual border with Russia.Health in the South Caucasus
Knowledge of Russian in Azerbaijan
შიდა მიგრაცია საქართველოში: რა ვიცით მის შესახებ CRRC-ის კავკასიის ბარომეტრის მონაცემების საფუძვლეზე?
არსებული შეფასებების თანახმად, მსოფლიო მასშტაბით შიდა მიგრანტთა რაოდენობა ბევრად აღემატება საერთაშორისო მიგრანტთა რაოდენობას. სამწუხაროდ, საქართველოში ძალიან ცოტა მონაცემი არსებობს შიდა მიგრანტების რაოდენობისა და მათი გეოგრაფიული განაწილების შესახებ. საქართველოს სტატისტიკის ეროვნული სამსახურის შინამეურნეობების ინტეგრირებული გამოკვლევები რეგულარულად აგროვებს ინფორმაციას ქვეყანაში შიდა მიგრაციის შესახებ. სახელმწიფო სერვისების განვითარების სააგენტო კოორდინაციას უწევს მოსახლეობის რეგისტრაციას საცხოვრებელი ადგილის მიხედვით.In the South Caucasus, the Enemy of my Enemy is my Friend
Emigration, Language, and Remittances in Georgia
Georgians Have High Hopes but Little Information about the Association Agreement with the EU
The Wave of the Future: Optimism, Pessimism and Fatalism in Georgia
Do Armenians Still View Integration with the EU as Part of a Positive-Sum Game?
On September 3rd 2013 Armenian President Serzh Sargsyan surprised many observers, including some in his own government, when he announced that Armenia would sign an agreement with Russia to join the Eurasian Customs Union (ECU) and spurn a long-negotiated Association Agreement (AA) with the European Union. The move has been dubbed a “U-Turn” as well as a “sudden shift in policy,” although it was predated by landmark Armenian-Russian agreements in 1997 and 2006.SME Performance in Georgia and Armenia: Part 1
Does public opinion accurately gauge government performance in the South Caucasus?
Household income and consumption patterns in Georgia
ODA Keyword Search
Georgia and the EU’s Economic Woes
Blood Donation in Georgia: Obstacles and Opportunities
Nagorno-Karabakh: Prospects for a Difficult Reconciliation (Armenia)
Spreading the News: File Sharing through Mobile Phones in Armenia
The Caucasus Barometer 2010 Dataset Is Available!
ODA – CRRC Data Analysis Online
PERCEIVED POVERTY IN GEORGIA: RESULTS OF THE 2011 CAUCASUS BAROMETER
The 2011 Caucasus Barometer asked the Georgian population, “Relative to most of the households around you, would you describe the current economic condition of your household as very good, good, fair, poor or very poor?Class in the Caucasus | Article by Ken Roberts and Gary Pollock
Fancy Living Abroad? 39% of Young Armenians Say "Preferably Forever"
Gender | How Does the South Caucasus Compare?
Labor Migration Article | Zvezda Dermendzhieva
Can a Cut NATO Supply Route Through Russia Benefit Georgia and Azerbaijan?
Insight to Georgian Households | CRRC Data on Economic Wellbeing in the Caucasus
Obstacles for Civil Society Development in the South Caucasus
Top Ten Leisure Activities in Georgia
Social networks in rural and urban Georgia
New Policy Advice on Migration and Development in Georgia
2010 Big Mac Index | Increased differences between Baku and Tbilisi
The Level of Trust in Government Institutions in Georgia: The Dynamics of the Past Three Years
Caucasus Barometer | A New Name for the CRRC's Data Initiative
Language Learning in Georgia
Greatest Threats Facing the World | Data from the 2009 CB & the Global Attitudes Survey
From environmental catastrophe to violence, our world currently faces serious challenges with long-term consequences. In this context, what do people in the Caucasus consider to be the most acute problems?
Attitudes toward the West | Caucasus Analytical Digest
Respondent Evaluation | A Great Tool for Looking into Survey Interviews
Ask CRRC!
Aleksey Hovakimyan on Rural & Economic Development in Armenia
Is the Caucasus in Europe or Asia? | Tim Straight at TEDxYerevan
Alpha Version of CRRC Data Initiative now online!!!
Inflation in Armenia? | Lecture by IMF Representative
Brookings Index of Regime Weakness | State Rebuilding or State Collapse in the Caucasus | The Annals of Data
Tourism: Structure and Cost-sharing
Parliamentary Elections in Georgia | ODIHR Observation
Georgian Election | ODIHR Preliminary Report and its Percentages
What do Georgian Troops Think about the Iraq War?
Study of Economic Relations Between Georgia and Armenia
Religious practices across the South Caucasus | the Data Initiative
Religious practices across the South Caucasus | Take two
European Cup Craze : Who Supports Whom in the Caucasus?
Maths in Armenia | comparing through TIMSS
CRRC Publication Research Fellowship 2008 Available
Caucasus Data | Language: Russian versus English?
Caucasus Data: Tolerance towards Others
Georgia: Women's Participation in Politics
Doing business in Azerbaijan: easy in theory
Credit Crisis in the Caucasus?
The August Conflict | Economic Impact on Georgia?
Polling Data on Turkish-Armenian Bilateral Relations
Focus on non-oil tax policy as oil revenues predicted to decline
How Supply fails Demand | Pots of Honey
South Caucasus Data 2007 on Unemployment
Mapping Development | WRI's "Funnel the Money"
The World Resources Institute, a global environmental think tank based in Washington DC, is providing maps that allow a visual comparison of data for the countries in the South Caucasus. Called "Funnel the Money", it seeks to chart development within countries, and also track allocation of resources from the central government by providing regional comparisons.Comparing Civic Participation: Caucasus Data 2007
EBRD Life in Transition Survey | worth analyzing!
Snapshots on Attitudes towards Education
"The Economic Dynamics of the Countries of the South Caucasus"
Civil Society in Post-Soviet Armenia
The study and analysis of civil society and civic participation is a fundamental way of better understanding a region and its processes of development and democratization. Researcher Babken Babajanian has studied civil society and civic participation in post-Soviet Armenia.Free Economic Zones in Georgia
Economic free zones in Georgia are no longer a necessary, helpful, or even relevant option for Georgia’s economic development according to a GFSIS article written by Vladimer Papava. A free economic zone is a discreet area of a country’s economy designated by the government and bestowed with certain benefits and privileges.Debts and Loans in Georgia (Part 1)
In Georgia, where, according to the World Bank, a third of the population live on under USD 2.5 per day, poverty and unemployment are consistently considered the most important issues facing the country. For those who are struggling financially, borrowing is a widespread coping mechanism. While access to credit can have benefits, debt can also have psychological costs, such as increased stress and anxiety. CRRC’s 2015 Caucasus Barometer (CB) data show interesting patterns about having personal debts in Georgia. The first part of this blog post focuses on the characteristics of those who report having personal debts in Georgia, while the second part looks at the money lending patterns, as well as reported well-being of people who are owed money or who borrow itDebts and Loans in Georgia (Part 2)
The first part of this blog post showed that people who report being in a worse economic situation are more likely to have debts in Georgia. In the second part of this blog post, a new variable is added to the analysis, “Does anyone owe you any money?”Prioritizing the personal: People talk more about personal issues than political events
In general people are primarily interested in their own lives, rather than in social or political events. In other words, social and political events will, most probably, be overshadowed by events in one’s personal life. CRRC’s 2015 Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey data provides more detailed insights on this. In this blog post, we compare answers to two CB questions: “When you get together with your close relatives and friends, how often do you discuss each other’s private problems?” and “When you get together with your friends and close relatives, how often do you discuss politics / current affairs?” in Armenia and Georgia.Are Georgians as tolerant as they claim to be?
On 15 November, the Ministry of Culture announced it would give ‘Georgian tolerance’ the status of intangible cultural heritage. Historically, Georgia may have exhibited relatively high levels of tolerance, with many pointing to the reign of King David the Builder in the 12th century. David is celebrated for presiding over the start of the country’s golden age, and many point to his encouragement of other ethnicities settling in Georgia as a good example of Georgian tolerance.Visa liberalization: Which groups in Georgia are expected to benefit most from it?
The introduction of visa free travel to the Schengen zone countries for Georgian citizens was one of the most prominent news stories in Georgia in 2017. It was also highly publicized and presented by the country’s government as a significant achievement on the way to European integration. Do people in Georgia agree with this assessment? And which groups of the population does the public think will actually benefit from the opportunity? CRRC’s 2017 Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey results shed some light on these questions.რა ფაქტორები უწყობს ხელს კარგი სამსახურის შოვნას? მოსაზრებები სომხეთსა და საქართველოში
რა ფაქტორები უწყობს ხელს კარგი სამსხურის შოვნას? ეს კითხვა მთელ მსოფლიოშია მნიშვნელოვანი, განსაკუთრებით კი ქვეყნებში, სადაც მაღალი გაცხადებული უმუშევრობაა. სომხეთი და საქართველო ასეთი ქვეყნების რიცხვს მიეკუთვნება. იმის გასაგებად, თუ სინამდვილეში რა ეხმარება ადამიანებს კარგი სამსახურის პოვნაში, საჭიროა კონკრეტულ ქვეყნებში შრომითი ბაზრის სიღრმისეული კვლევა. თუმცა, აგრეთვე საინტერესოა ხალხის მოსაზრებები ამ საკითხთან დაკავშირებით. CRRC-ის 2017 წლის კავკასიის ბარომეტრის კვლევის ფარგლებში მოსახლეობას სომხეთსა და საქართველოში ჰკითხეს, თუ რა ფაქტორებია მნიშვნელოვანი კარგი სამსახურის საშოვნელად მათ ქვეყნებში.People in Georgia approve of doing business with Russians, despite interstate hostility
In the 2017 wave of CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey, 40% of the population of Georgia named Russia as the main enemy of the country. Turkey and the United States garnered the second highest share of responses with 3% each. Yet, no particular animosity towards ethnic Russians is observed in answers to a question about people’s (dis)approval of individuals of their ethnicity doing business with Russians. This blog post examines how answers differ by people’s opinions about whether or not Russia is the main enemy of Georgia.Changes in public opinion between 2011 and 2017
A lot changed in Georgia between 2011 and 2017, including the government. New promises and new regulations have been made and new priorities set by politicians. A visa free regime with the Schengen zone countries came into force. An ultranationalist ‘Georgian March’ was organized. A Georgian priest was charged with conspiracy to murder the Secretary of the Patriarch of the Georgian Orthodox Church, the most trusted institution in Georgia. This list is by no means exhaustive, but it does raise questions about whether and how public opinion has changed against the backdrop of these and other events.Which groups name Russia as Georgia’s main enemy?
In 2017, 40% of the population of Georgia named Russia as the main enemy of Georgia. Yet the opinion that Russia is the main enemy of the country is not equally present in different demographic groups. This blog post uses data from CRRC’s 2017 Caucasus Barometer survey to gain a better understanding of the characteristics of those who report Russia is the country’s main enemy.During Sargsyan’s incumbency, dissatisfaction with government grew and support for protest increased
Serzh Sargsyan, formerly the President and then Prime Minister of Armenia, resigned from office on April 23rd, 2018, following 11 days of peaceful protest. Over the past 10 years, which coincide with Sargsyan’s time in office, Armenians were increasingly dissatisfied with their government. At the same time, the country witnessed growing civic engagement, with “youth-driven, social media-powered, issue-specific civic activism,” referred to as “civic initiatives”. CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer data from 2008 to 2017 reflect both these trends.Willingness to temporarily emigrate from Armenia and Georgia: Does fatalism matter?
Scholarship points to a number of factors that contribute to an individual’s willingness to emigrate, either on a temporary or permanent basis. Political, economic, and social conditions are all important variables in the emigration equation. This blog post uses data from CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey to see whether or not people who express a willingness to temporarily emigrate from Armenia and Georgia differ from others in terms of the reported belief that people shape their fate themselves. Those who believe so may be more inclined to consider actions such as temporary emigration.Five data points about homophobia in Georgia five years after the IDAHOT riot
Five years ago, on May 17, 2013 a homophobic riot took place in Tbilisi in response to a small LGBTQ rights demonstration on the International Day against Homophobia and Transphobia. Thousands of protestors, including frocked priests, chased the demonstrators through the streets of Tbilisi as police struggled (some say facilely) to protect the demonstrators from violence. In the time since, LGBTQ rights have remained on the agenda in Georgia, with an anti-discrimination law passed in 2014, which gives some protection to LGBTQ people, and the first openly homosexual candidate running for office in the 2017 local elections. Despite this progress, homophobic and transphobic violence still occurs in the country (for example, see here, here, and here). Five years after the events of May 17, 2013, this article presents five findings from CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey about homophobia in Georgia.Perceptions of the problems faced by women in Georgia
People in Georgia consistently name unemployment as the main problem the country faces. Women, compared with men, report having a job less often. Based on CRRC/NDI December 2017 survey findings, this blog post presents the population’s perceptions of some of the issues that women in Georgia face that may partially explain women’s lower labor force participation rate.Willingness to temporarily emigrate from Armenia and Georgia: Does education matter?
A previous CRRC blog post showed how people’s willingness to temporarily emigrate from Armenia and Georgia varied according to their belief in whether everything in life is determined by fate or people shape their fate themselves. The blog post concluded that compared to people who are not interested in temporary emigration from these countries, those who are tended to believe slightly more often that people shape their fate themselves.Do people in Georgia see the government as a parent or as an employee?
Based on CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey data, this blog post describes how people in Georgia see the government, as a “parent” or as an “employee”, and how this differs by settlement type, gender, and education level.The Caucasus Barometer survey regularly asks people, “Which of the following statements do you agree with: “‘People are like children; the government should take care of them like a parent’ or ‘Government is like an employee; the people should be the bosses who control the government.’” Approximately half of the population of Georgia (52%) agreed in 2017 with the former statement and 40% with the latter. Responses to this question have fluctuated to some extent over time, but overall, attitudes are nearly equally split.
Is Georgia’s Orthodox Christian population losing (trust in) their religion?
Surveys conducted in Georgia have repeatedly shown that the Georgian Orthodox Church’s leader Patriarch Ilia II is the most trusted public figure in the country. Yet, CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey data from 2008 to 2017 suggests that both the share of Orthodox Christians in Georgia that trust the Church and the degree to which they trust the Church is on the decline. Although the survey does not provide direct evidence, the scandals surrounding the church in recent years could have contributed to this. For instance, in 2017, a priest was convicted of attempting to poison the Secretary of Ilia II. The government has sold land to the Church at symbolic prices on numerous occasions, often leading to negative media coverage. In 2013, priests were involved in an anti-LGBT rights riot.Views on marital (in)fidelity in Georgia
According to 86% of adults in Georgia, cheating on one’s spouse can never be justified, according to CRRC’s 2017 Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey findings. Another 12% also reported disapproving of cheating, but refrained from a radical “never” answer and choose relatively softer options. Only about 2% openly agreed, albeit with different strength of agreement, with the position that cheating on one’s spouse can be justified. While these answers are expected to be influenced by social desirability bias, they are still interesting indicators of views on marital (in)fidelity in Georgia. Importantly, the distribution of answers has been quite stable since 2011.Pension reform is underway in Georgia, but only about half of the population is aware of it
On July 21, 2018 Georgian legislators approved an accumulative pension scheme, after years of discussion. As one of the requirements of the new law, employees with contracts who are under the age of 40 have to contribute 2% of their remuneration to the state-run pension fund, on a monthly basis. Although other employees are not legally required to do so, they may participate in the scheme voluntarily. This law is a first step in a larger reform of Georgia’s pension system. Opposition politicians have criticized the new law citing that it counters the country’s constitution as it introduces a new tax without a referendum. Several civil society groups also expressed criticism of the reform, questioning its legitimacy.Which questions do people tend to respond “Don’t know” to?
On surveys, sometimes the questions asked are hard for some people to answer. As a result, the answer option “Don’t know” is a regular part of any survey dataset. But are some questions particularly likely to elicit these responses? This blog post uses un-weighted 2017 CRRC Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey data for Georgia to look at this question.Budget priorities are similar to people's spending priorities
Georgia’s state budget amounted to GEL 12.5 billion in 2018. The Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs; Ministry of Regional Development and Infrastructure; and Ministry of Education and Science had the largest appropriations at 28.2% (GEL 3.528 billion), 14.5% (GEL 1.815 billion), and 9.5% (GEL 1.186 billion) of the budget, respectively. In the 2018 June CRRC/NDI survey, respondents were asked, “What are your top three priorities for spending, understanding it means cutting elsewhere?” Respondents were provided with a show card and allowed to name up to three answers. This blog post looks at whether responses match up with actual spending, and how priorities vary among different demographic groups.Attitudes towards the new banking regulations
The share of the public with loans from formal financial institutions doubled from 2011 to 2016 according to World Bank Group’s analysis based on Integrated Household Survey in Georgia. The July 2019 CRRC/NDI survey data suggests that about half of the population has a loan. To address perceived over-indebtedness, on 1 January, 2019 the National Bank of Georgia introduced new regulations, restricting lending without more extensive analysis of a consumer’s solvency. The analysis includes looking at an individual’s income, expenses and total obligations, and determination of debtors’ capacity to service their loans without significant financial difficulties.How widespread is homophobia in Georgia?
Homophobia is widespread in Georgia. The homophobic riots that occurred on the International Day against Homophobia in 2013 and the bedlam that took place surrounding the planning of the 2019 Pride Parade exemplify this.Know English and how to use a computer?
A slightly jeering expression in Georgia when speaking about employment prospects suggests that to get a job, you need to know English and how to use computers. Data from Caucasus Barometer 2019 shows there’s a bit of truth in the jest.Why are Georgians Nostalgic about the USSR? Part 1
Several surveys in recent years suggest that close to half of the Georgian public considers the dissolution of the USSR a bad thing. After nearly 30 years since gaining independence, why do so many Georgians look back with nostalgia towards the Soviet Union? Reasons for Soviet nostalgia in other contexts are usually associated with how people experienced transition from state socialism to capitalism. The economic hypothesis explaining nostalgia argues that a perception of being part either “a winner” or “a loser” of the transition is associated with nostalgic feelings towards the Soviet Union. Other hypotheses introduce politics into the equation. According to this explanation, those who reject democracy on ideological grounds are more likely to be nostalgic as are those who think that democratic institutions are too feeble in delivering state services. Are these explanations true for Georgian Ostalgie? This series of blog posts explores these and other potential explanations to Soviet nostalgia.Are Lion’s Whelps Equally Lions?!
In Georgia, tradition has it that a son stays in the family and is responsible for taking care of his parents in their old age. Consequently, tradition also gives parents’ property to their sons. This limits women’s access to economic resources. New data from Caucasus Barometer shows that regardless of whether people think that a son or daughter or both equally should take care of their parents in their old age, many believe the son should still get the inheritance.აღწერაში დაკარგულები: მეგრული და სვანური ენები საქართველოში გაქრობის საფრთხის ქვეშ არიან
21 თებერვალს საქართველო მშობლიური ენის დღეს აღნიშნავს, თარიღს, რომელიც იუნესკომ „ლინგვისტური და კულტურული მრავალფეროვნებისა და მრავალენოვნების ხელშეწყობის“ მიზნით დააწესა.
Coming Together and Growing Apart: A Decade of Transformation in the South Caucasus
CRRC is excited to announce its 6th Methods Conference, which will be held on June 26-27 and open to public viewing over Facebook and direct participation through signing up here. The conference focuses on a decade of change in the region.The most important issues facing Georgia, prior to the COVID-19 outbreak
სოციალური კაპიტალი საქართველოში: როგორ მყარდება ნდობა საქმით
There is a gap between support for democracy and liberal values in Georgia
Public opinion polls suggest support for democracy is on the decline in Georgia, but does support for democracy correlate to support for liberal values?
An increasing number of Georgians view their country as ‘a democracy with major problems’, with CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey showing the share of people reporting this belief to have increased from 27% in 2011 to 48% in 2019.
In parallel to this growing scepticism towards the country’s democratic situation, surveys show a decline in the proportion of the population believing that democracy is preferable to any other kind of government, falling from 65% in 2011 to 49% in 2019.
Lockdown vs re-opening the economy in Georgia
As the number of new daily confirmed cases is again on the rise, we look at how people felt about the anti-coronavirus restrictions in May.
Aside from the public health situation, COVID-19 has led to rising unemployment, reduced incomes, and food insecurity in Georgia. As the number of new daily confirmed cases is again on the rise, the Caucasus Datablog takes a look at how people felt about the anti-coronavirus restrictions when they were at their height.
Conservative gender mores are changing in Georgia
Gendered norms prevail in Georgian society, which often translates into deprecation of women for smoking, drinking alcohol, having pre-marital sex, and even living with a boyfriend. However, attitudes appear to be shifting.
CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey asked people what they thought about several such activities. The data showed that the public are least accepting of women smoking, with 80% reporting it is never acceptable at any age. Sexual relations (63%) and cohabitating with a man before marriage were also commonly thought to be never acceptable for women (60%).
More Georgians than ever own phones and TVs, but inequalities remain
Gaps remain in mobile phone ownership in Georgia
While mobile phone ownership is widespread in Georgia, gaps still remain among rural, elderly, and ethnic minority populations.
Owning a mobile (cell phone) is considered so important that more widespread ownership is considered a sustainable development goal (SDG 5.b) by the United Nations.
Mobile phone ownership among households has increased significantly over the last decade. Caucasus Barometer data indicates that in 2008, two thirds of households owned a mobile phone. This has steadily increased, reaching 96% of households in 2019, the last year for which Caucasus Barometer data is available.
უცნაურია, თუმცა, პანდემიის დროს უფრო მეტი ადამიანი გრძნობს თავს ჯანმრთელად
კორონა ვირუსის პანდემიამ აშკარად დააზიანა ხალხის ჯანმრთელობა.თუმცა, კავკასიის ბარომეტრის კვლევის ახალი მონაცემების მიხედვით, 2020 წელს ადამიანები საკუთარ ჯანმრთელობას უფრო კარგად აფასებენ, ვიდრე წინა წლების გამოკითხვებში.
2019 წელს მოსახლეობის მხოლოდ 35% აფასებდა თავის ჯანმრთელობას კარგად. გასულ წლებში, ეს მაჩვენებელი იცვლებოდა, თუმცა, ყველაზე დიდი ცვლილება 2013-2014 წლებში მოხდა, როდესაც ეს მაჩვენებელი 41%-დან 30%-მდე შემცირდა. ამის საპირისპიროდ, 2019 და 2020 წლების გამოკითხვებს თუ შევადარებთ, ადამიანების წილი, ვინც საკუთარ ჯანმრთელობას კარგად აფასებს, თითქმის გაორმაგდა - 35%-დან 65%-მდე გაიზარდა.
War in Nagorno-Karabakh went unnoticed for a quarter of Georgians
The recent war in Nagorno-Karabakh resulted in thousands of deaths and the displacement of tens of thousands. Yet despite there being a brutal war near its borders, many in Georgia were unaware of the conflict.
Data from the Caucasus Barometer survey indicate that awareness of the conflict’s existence increased shortly after the war in 2020 compared to 2013, but only slightly. In 2013, when the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict was ‘frozen’, 66% of Georgians reported they had heard of it. Around a third of the population was not aware of it. In December of 2020, shortly after the 44-day long war, 74% of Georgians reported they had heard of it. A whole quarter (26%) of the population, meanwhile, was not aware of military operations between the country’s two direct neighbours.