Note: This article first appeared on the Caucasus Data Blog, a joint effort of CRRC-Georgia and OC Media. This article was written by Eto Gagunashvili, a Researcher at CRRC-Georgia and Nino Topchishvili, a Junior Fellow at CRRC-Georgia. The views presented in the article are the author’s alone and do not necessarily represent the views of CRRC Georgia, Caucasian House, or any related entity.
More than half of the Georgian public support a gender-balanced parliament, with women, young people, and those not aligned with the ruling party more in favour of a 50/50 gender split.
Legislation passed in Georgia in 2020 required parties to nominate at least one out of every four candidates on their electoral lists be women, to their electoral lists, with this number increasing to one in three by 2028, promoting women’s participation in politics. However, due to the first-past-the-post component of elections, less than one quarter of current parliamentarians are women.
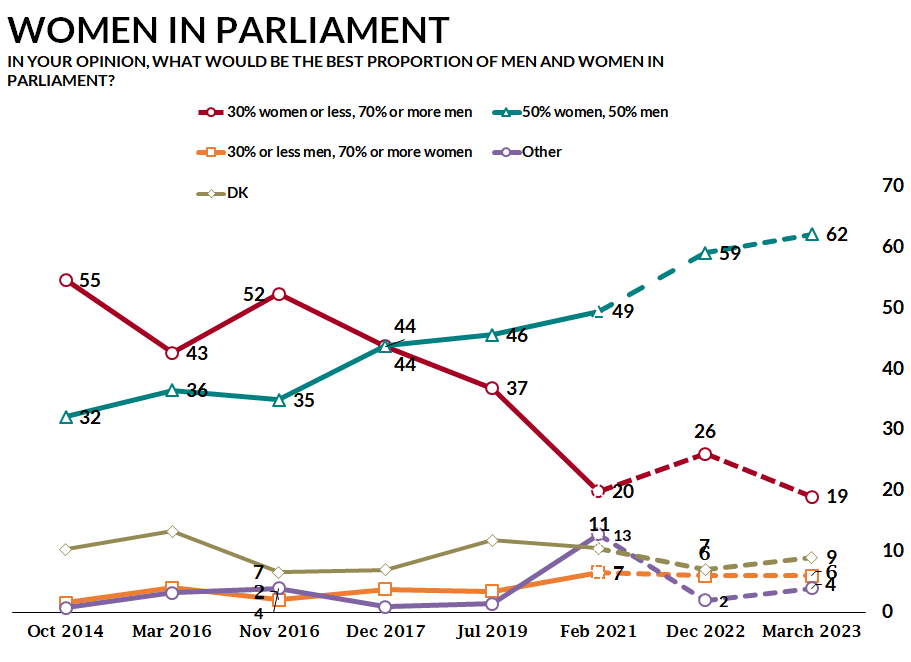
In parallel to legislative changes, public opinion is becoming more supportive of women in leadership positions, with CRRC and NDI’s surveys from 2014 to the present showing a consistent increase in the share of the population that believes that an equal gender split in parliament is ideal.
Since 2022, a majority of the Georgian public has reported that the ideal proportion of men and women in parliament is 50% male and 50% female.
The share of the public supporting this position rose from 49% to 59% between 2021 and 2022, remaining at a similar level of 62% in 2023. By comparison, only 32% reported agreeing with this position in 2014.
The rise in people reporting an equal split between men and women in parliament coincides with a decline in the share of people reporting that 30% or less women and 70% or more men would be the ideal share. This percentage dropped from 55% in 2014 to 19% in 2023.
Women are 13 percentage points more likely to support an equal share of men and women in parliament than men. Older people (55+) are 12 percentage points less likely to support a gender-balanced parliament compared to young people (18-34).
People who report that there is no party close to them are 12 percentage points more likely to choose equal representation of men and women in parliament than Georgian Dream supporters.
Education level, settlement type, ethnicity, and wealth are not associated with support for an equal share of men and women in parliament, controlling for other factors.
The above data show that the public is increasingly in favour of having more women in Georgia’s parliament, with women, people under 55, and those who do not support Georgian Dream most in favour of that.