While Georgia has yet to be officially declared an upper middle income country by the World Bank, as a result of the 2014 census, it’s likely to be labeled one after the final census results are published in April of…
ეკონომიკური მდგომარეობა
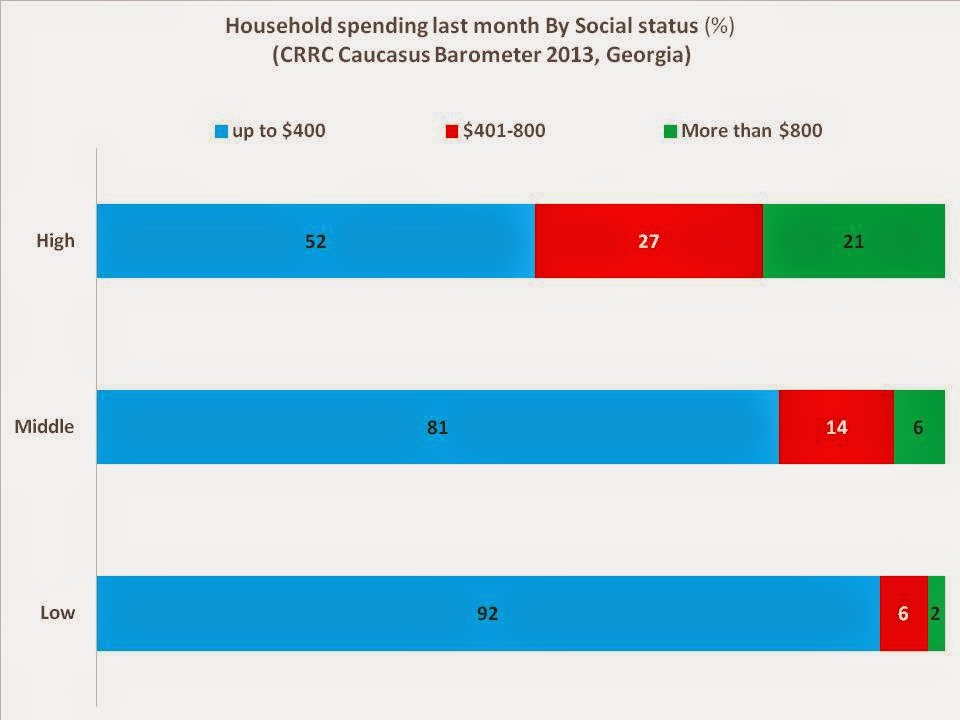
This blog post examines how social status is associated with individual and household well-being
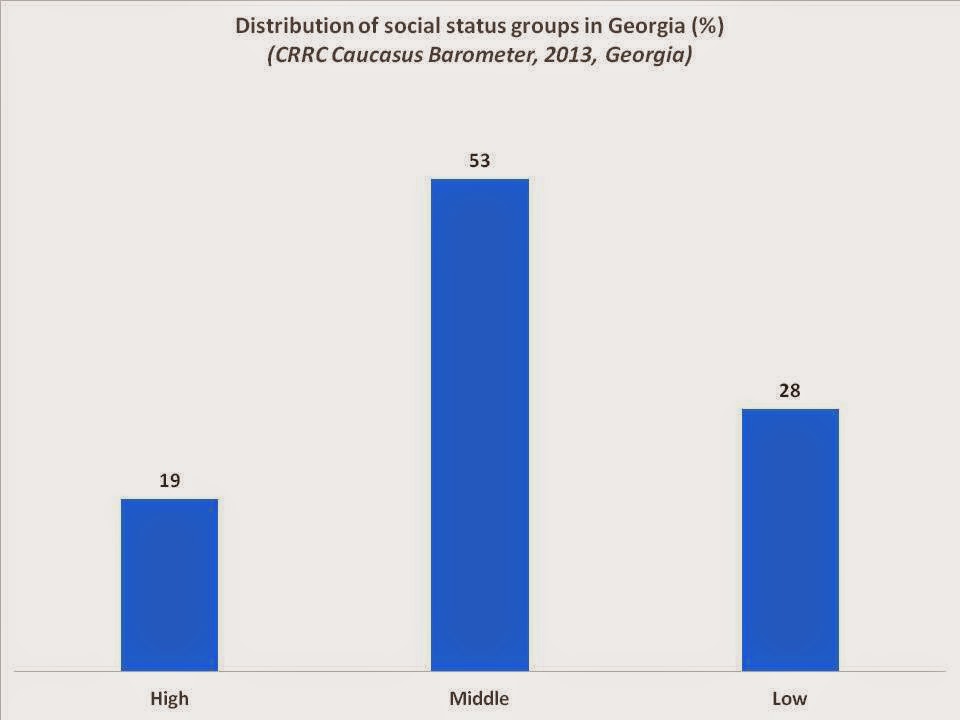
Taxi drivers tell perhaps the most telling story of Georgia’s economic transition. They often complain that the transition made their high social status useless, thus pushing them into taxi driving. This often heard and mocked complaint highlights the contrast between…
As discussed in the first blog post of this series, the results of the CRRC Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey show that Georgians demonstrate higher levels of interpersonal and institutional trust than Armenians. These types of trust are important indicators of social capital,…
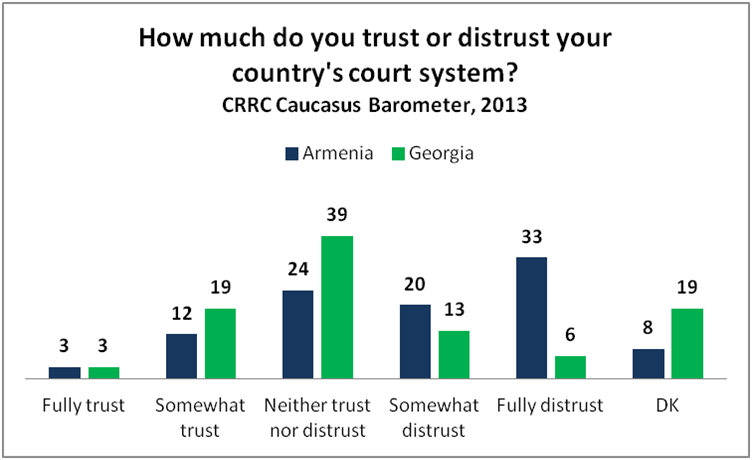
The CRRC Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey results demonstrate that Georgians exhibit relatively high levels of interpersonal and institutional trust when compared to their Armenian neighbors. Trust is an important component of “social capital,” which is widely perceived to be a necessary…
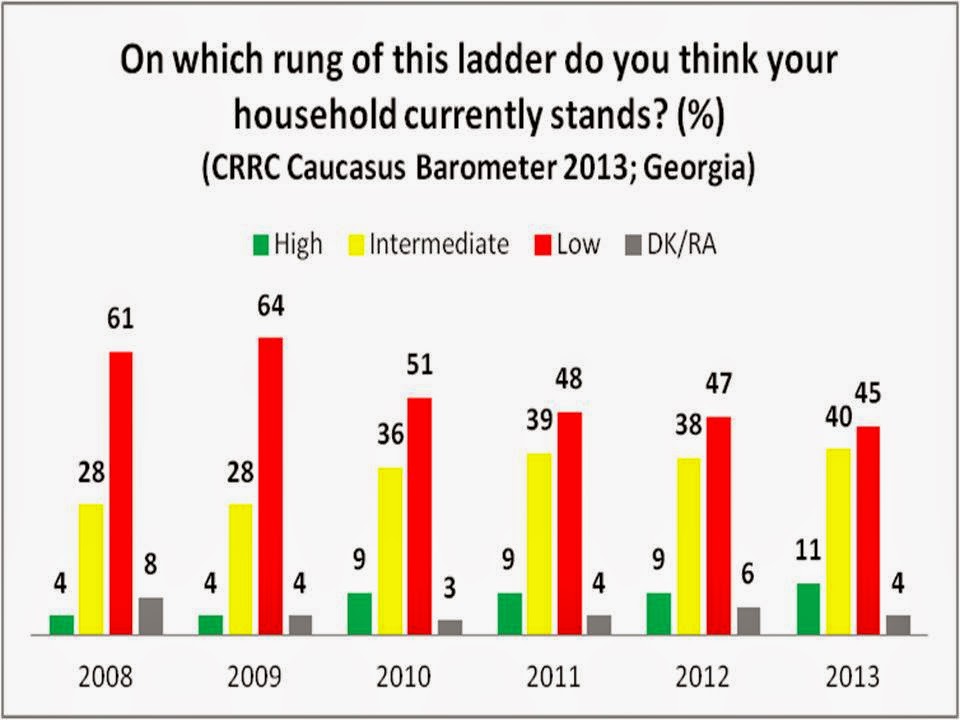
A recent CRRC regional blog post analyzed the presence of fatalism in Georgia. The post cited CRRC Caucasus Barometer (CB) data which shows that in 2013, 28% of Georgians agreed that “everything in life is determined by fate.” While the CB findings…
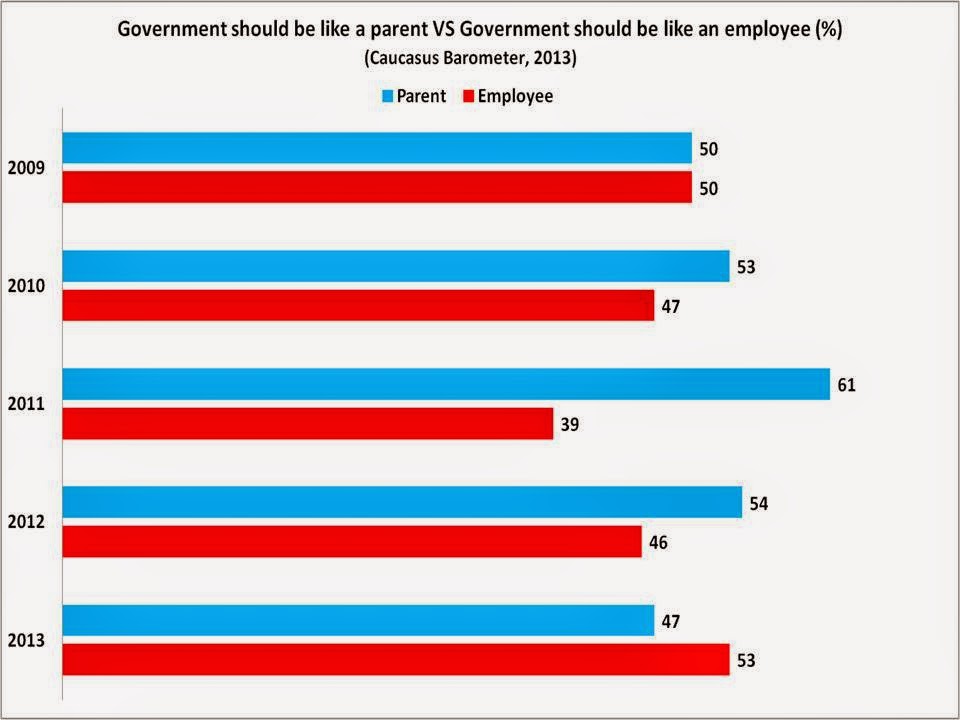
According to the Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, paternalism is “the interference of a state or an individual with another person against their will motivated by a claim that the person interfered with will be better off or protected from harm”…
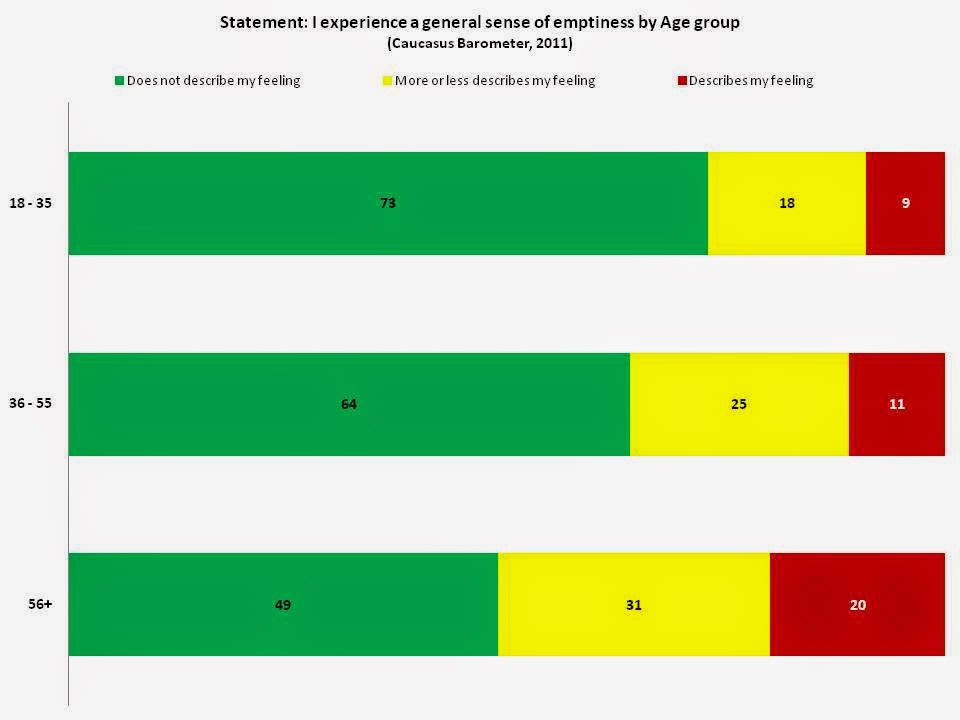
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), “Multiple social, psychological, and biological factors determine the level of mental health of a person at any point in time. In addition to the typical life stressors common to all people, older people are more…
