Russia as a threat: the Ukraine crisis and changing public opinion in Georgia
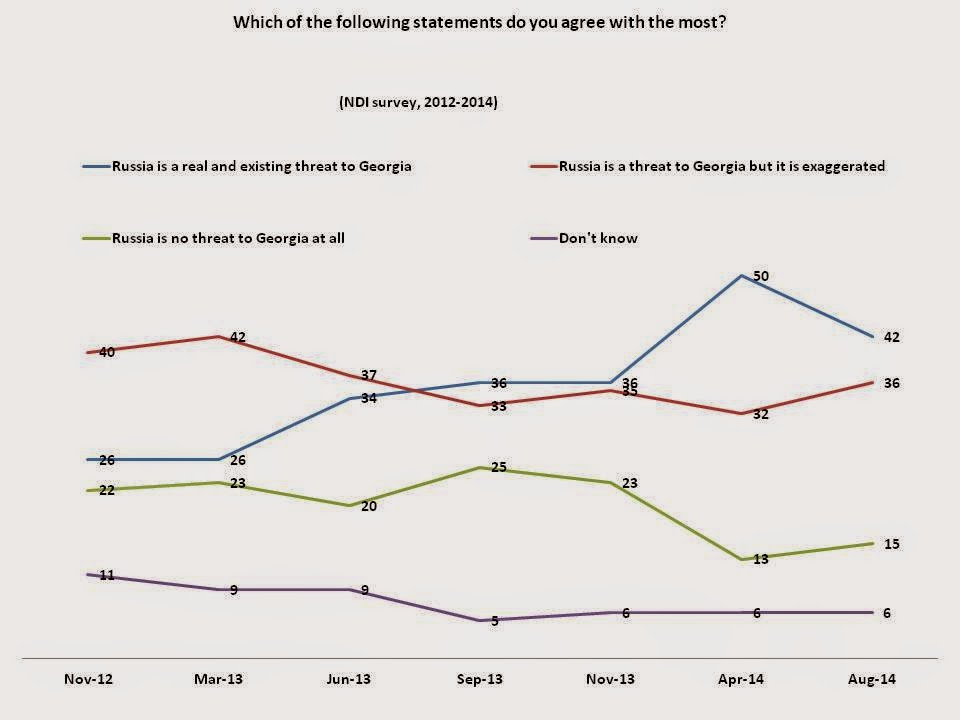
When thinking about Russian and Georgian relations after the 2012 parliamentary elections there are a number of important events to take into consideration: the initiation of Georgian-Russian dialogue in the form of the Abashidze-Karasin negotiations, the re-opening of the Russian market to Georgian products, and the so-called borderization of South Ossetia. Obviously, the opening of Russian markets and direct bilateral negotiations are not likely causes of increased negative attitudes toward Russia, while Georgians are against the borderization policy making it a potential cause of negative attitudes towards Russia. Notably, the so-called borderization policy, which started in May of 2013, marks the beginning of a shift in attitudes toward Russia.
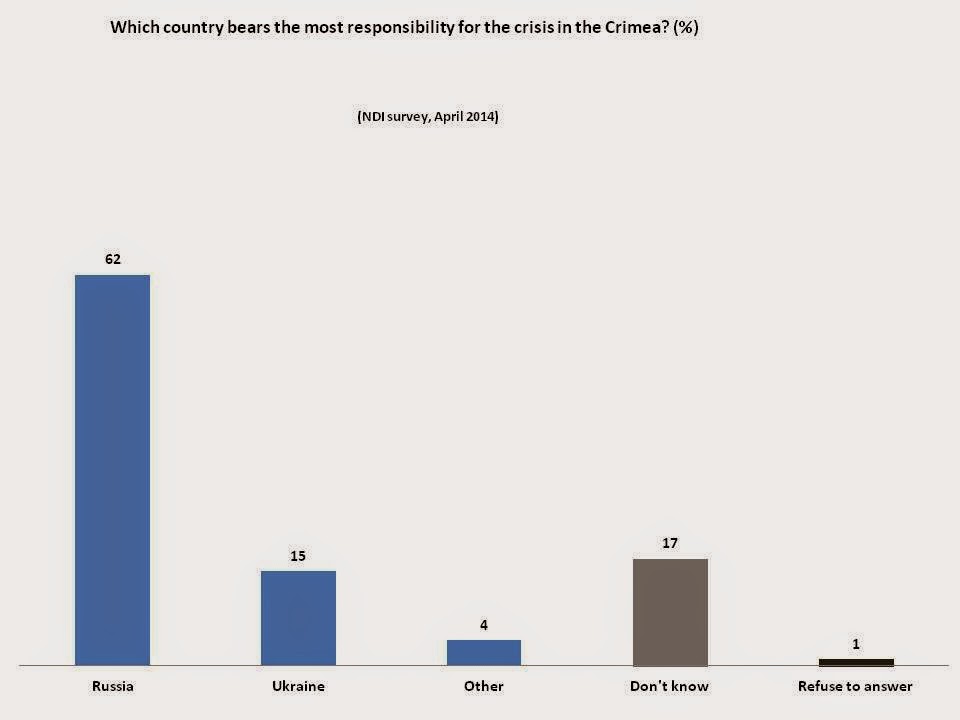
Another important event that may be associated with changes in public opinion is the crisis in Ukraine. While the Ukraine crisis is not directly tied to Georgian-Russian relations, Tbilisi has consistently expressed its support for Ukraine and its territorial integrity. Since the crisis there has been a very apparent change in Georgians’ perceptions of Russia as a possible threat. This is further exemplified by the responses to a question on NDI’s April 2014 survey- “which country bears the most responsibility for the crisis in Crimea?” As the graph below shows, 62% of Georgians consider Russia the country which bears the most responsibility for the crisis in the Crimea. Moreover, 66% of Georgians find Crimea’s unification with Russia unacceptable. It is noteworthy that the events in Ukraine which most experts assess as a direct and open Russian aggression against Ukraine started in March of 2014, directly before the April 2014 survey.
It is interesting that in August 2014, support for the statement that “Russia is a real and existing threat to Georgia” declined by 8% compared to April. This could mean that Russia appeared to be more threatening to Ukraine (and hence to Georgia) at the onset of the crisis, rather than now as the conflict has protracted in time. Russia's role in fueling the crisis in Ukraine may remind Georgians of Russia’s intervention in the separatist conflicts in Abkhazia and South Ossetia in the 1990s or of the 2008 August war with Russia. In sum, it seems that the events in Ukraine aggravated the sense of a potential future threat from Russia, especially considering the similar Euro-Atlantic policy orientations of both Ukraine and Georgia.
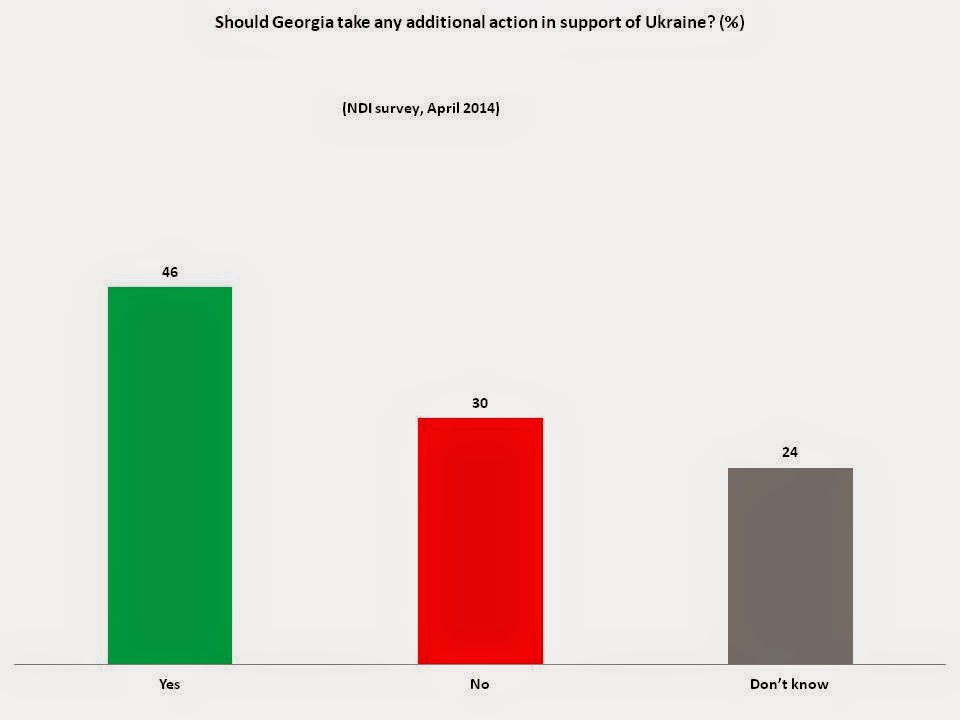
Considering the above, it is not surprising that almost half of the population (46%) believes that the actions taken by the Government of Georgia in support of Ukraine are insufficient and additional actions are needed. Notably, 63% of the population approved of the Georgian government’s condemnation of Russia’s actions in the Crimea.
This post has looked at the impact which events in Ukraine have had on the perception of threat expected from Russia. It appears that the increased level of agreement with the statement that “Russia is a real and existing threat to Georgia” in April may be linked to the ongoing crisis in Ukraine. This is supported by the fact that most Georgians believe that Russia bears responsibility for the crisis in Ukraine and that Georgians are against Crimea’s unification with Russia. How Georgian public attitude will change toward Russia and whether the crisis in Ukraine will continue to influence it remains to be seen, but readers interested in exploring the issues discussed above can delve further into Georgian perceptions of Russia here.
By Edisher Baghaturia
Ethnic minorities, Georgians, and foreign policy orientation
Getting to the streets: Who is more inclined to protest in Georgia?
Corruption in the South Caucasus
Corruption and paying a bribe was not uncommon in the former Soviet Union. However, following the collapse of the USSR, rampant corruption began to permeate virtually every aspect of daily life in newly independent Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia (Sandholtz and Taagepera 2005). Reports by international organization...Georgian Foreign Policy: Continuity or Change?
The results of the October parliamentary elections in Georgia have raised questions regarding the future trajectory of Georgian foreign policy. One of the priorities of Georgian foreign policy has been European and Euro-Atlantic integration. Will the new Georgian government initiate major changes and redirect Georgia’s foreign policy that has been supported by the National United Movement? Will Ge...Youth and Politics in Georgia
Since 2011, CRRC has been involved in the Memory, Youth, Political Legacy, and Civic Engagement (MYPLACE), a four-year project funded by the European Commission. The project aims at exploring young people’s social participation in Georgia influenced by historical contexts of totalitarianism and populism in Europe. Among others, the objectives of the MYPLACE project include (1) conceptualization of...The Fury Before the Storm
The blog analyzes if the special precinct really mattered for the Sagarejo by-elections or wether it was the ethnic voting patterns, which explain the differences.
Georgia—Abkhazia
The Olympics in Sochi, Russia, took place about 30 kilometers from Russia’s border with the separatist region of Abkhazia in Georgia. As a security precaution, the Russian government has temporarily moved its border 11 kilometers into Abkhazia to create a “security zone,” at which travelers entering will have to show identification before proceeding to the actual border with Russia.Can’t get no satisfaction. Who doesn’t want to join the EU?
Russia, Georgians, and the State
How to buy votes when you can’t buy votes
Before and After the Elections: Shifting Public Opinion in Georgia
Alternating Pasts, Changing Futures
Note: This blog is re-posted from the MYPLACE project's blog. The original MYPLACE blog can be found here.Knowledge of Russian in Azerbaijan
Electoral Notes- Municipal Elections, 2014
Trust in local government in Georgia
A New CRRC-Georgia/PROLOG Report: Legal Professionals' Views on the Legal System
CRRC-Georgia’s report The Judicial System in Georgia: Views of Legal Professionals was published on 11 July, 2016. The report details the results of a baseline study for the USAID-funded project Promoting Rule of Law in Georgia (PROLoG) implemented by East-West Management Institute (EWMI).A look at (in)Justice in Georgia as charges are brought against ex-President Saakashvili
Changing issue salience in Georgia after 2008
Do Armenians Still View Integration with the EU as Part of a Positive-Sum Game?
On September 3rd 2013 Armenian President Serzh Sargsyan surprised many observers, including some in his own government, when he announced that Armenia would sign an agreement with Russia to join the Eurasian Customs Union (ECU) and spurn a long-negotiated Association Agreement (AA) with the European Union. The move has been dubbed a “U-Turn” as well as a “sudden shift in policy,” although it was predated by landmark Armenian-Russian agreements in 1997 and 2006.Georgia in a turbulent world: 2014 in review
What We Know About Volunteering in Georgia
[This post originally appeared in investor.ge]By Nino Zubashvili
The French Senate Bill and Armenian Perceptions on Turkey
Caucasus Barometer: Unpacking Public Trust in the President
MyPlace Website is up!
Georgia and Russia: Can positive relations between the populations overcome the political turmoil?
Does Refusal to Recognize Elections in Abkhazia Reduce Prospects for Resolution?
Is the South Caucasus a homogenous region?
Can a Cut NATO Supply Route Through Russia Benefit Georgia and Azerbaijan?
Georgia & Russia | Russian Analytical Digest
Counting Crowds & Crowds Counting | Jacobs' Method
During the last 25 years Georgian capital has experienced a diverse history of political meetings in its central areas including peaceful demonstrations, rallies with radical political demands, “tent towns” and so forth. The higher the attendance, the more legitimate the protests are often seen to be. As a result, the figures themselves usually are contested, sometimes in significant controversy.Social networks in rural and urban Georgia
South Ossetia: Enhancing the Public Debate
Who is Russia's Enemy? | Pew Research Center Data
Post-Soviet States’ Democratic Decline: Results from Freedom House Report
Georgian get-togethers: Private Problems versus Politics
In September 2011, CRRC on behalf of Eurasia Partnership Foundation and EWMI G-PAC conducted a nationally representative survey on Volunteerism and Civic Participation in Georgia. Georgians were asked how often they get together and discuss private problems and politics with their friends and relatives (who do not live in their houses).Is the Caucasus in Europe or Asia? | Tim Straight at TEDxYerevan
Food Safety in Georgia: views from retailers, producers and consumers in Tbilisi and Samtskhe-Javakheti
Alpha Version of CRRC Data Initiative now online!!!
USAID Political Party Assessment of Europe and Eurasia
Parliamentary Elections in Georgia | ODIHR Observation
Georgia post-Election Phone Survey | Quick Review
Caucasus Data | Language: Russian versus English?
Georgia: Women's Participation in Politics
Russian-Georgian Relations | Alex Rondeli on July 29
Georgia Post-Conflict Phone Survey | may be a first glance?
What do Russians think about the situation in Abkhazia and South Ossetia? -- Data Snapshot
Russian Public Opinion | Levada Update
The August Conflict | Economic Impact on Georgia?
Pre-Election Polls | what would be needed
With the election in Georgia approaching fast, polls are beginning to appear every week. Unfortunately, many of these polls are taken at face value. The reality is that at this point there is not a single pre-election poll that has demonstrated credibility. This does not ...Comparing Civic Participation: Caucasus Data 2007
World Press Freedom | Caucasus does badly!
Iakobashvili on the Current State of the Conflict
Gabala Radar Station -- local health awareness
Exit Polls | a good idea?
With upcoming elections in Georgia, the attention is back on a theme that otherwise often gets neglected: what does the Georgian electorate want?Georgia's Performance? | Millenium Challenge Corporation's Meta-Index
With all the attention on Georgia, it may be interesting to revisit Georgia's most recent performance as seen by international organizations. As it happens, the Millennium Challenge Corporation offers a such an assessment through its annual scorecard, just released last week. This scorecard is a meta-index, drawing on data from the World Bank Institute, Freedom House, IFC, WHO, UNESCO and a few other organizations.The Open Budget Index | Georgia, Azerbaijan and the World
The Open Budget Index, a project of the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities, released the first-ever independent and non-governmental Budget Transparency Ratings in October 2006. The index endeavors to provide the practical information needed to analyze the transparency and accessibility of a government’s budgetary processes—and thus better equip citizens and legislators in lobbying for governmental accountability and targeted, effective policymaking.Georgian parliamentary elections 2016 - Gender and ethnic minority representation on party lists
The results of the 2016 Parliamentary elections in Georgia reveal some interesting patterns about the representation of women and ethnic minorities in Georgian politics.Who makes political decisions in Georgia: What people think
Bidzina Ivanishvili resigned from the post of prime minister of Georgia on November 20th 2013, and in his own words, “left politics“. Speculation about his continued informal participation in the political decision-making process began even before he resigned and still continues. Some politicians think that Ivanishvili gives orders to the Georgian Dream party from behind-the-scenes, while others believe that he actually distanced himself from politics. Politicians, journalists and experts continue to discuss the situation. Meanwhile, a majority of Georgia’s population thinks that Bidzina Ivanishvili is still involved in the governing process and that his informal participation is unacceptable.Prioritizing the personal: People talk more about personal issues than political events
In general people are primarily interested in their own lives, rather than in social or political events. In other words, social and political events will, most probably, be overshadowed by events in one’s personal life. CRRC’s 2015 Caucasus Barometer (CB) survey data provides more detailed insights on this. In this blog post, we compare answers to two CB questions: “When you get together with your close relatives and friends, how often do you discuss each other’s private problems?” and “When you get together with your friends and close relatives, how often do you discuss politics / current affairs?” in Armenia and Georgia.Taking partly free voters seriously: autocratic response to voter preferences in Armenia and Georgia
Do voters in less than democratic contexts matter or are elections simply facades used to create a veneer of democratic accountability for domestic and international actors? Within the Autocratic Response to Voter Preferences in Armenia and Georgia project, funded by Academic Swiss Caucasus Net, CRRC-Georgia and CRRC-Armenia aimed to help answer this question, at least for Georgia and Armenia. On October 27, Caucasus Survey published the results of the project in a special issue, available here.Gender (in)equality on TV
Stereotypes are an inseparable part of every society, and present in many parts of everyday life. Georgian society is no exception in this regard. For example, some professions like teaching are stereotypically thought of as “women’s professions” while others like being a soldier are considered “men’s professions”. The media is considered one of the strongest means through which stereotypes are strengthened or broken. In Georgia, TV is the most important media, given that according to CRRC/NDI data, 73% of the population of the country name television as their primary source of the information. In order to understand the dynamics around gender-based stereotypes on TV, CRRC-Georgia monitored the main evening news releases and political talk shows broadcast during prime time (from 18:00 to 00:00) on five national and three regional channels from September 11 to November 12, 2017 (Channel One of the Public Broadcaster, Adjara, Rustavi 2, Imedi, Maestro, Trialeti, Gurjaani, Odishi) with the support of the UN Joint Program for Gender Equality with support from UNDP Georgia and the Swedish government.As many Georgians think the West spreads propaganda as Russia
On 13 February, the United States released its Worldwide Threat Assessment of the US Intelligence Community. In it, the significance of Russian influence operations in Georgia were highlighted. Just eight days earlier, on 5 February, a coalition of Georgia’s leading non-governmental organisations made an official offer to support the Government of Georgia, the EU, and NATO in their efforts to counter anti-Western propaganda.People in Georgia approve of doing business with Russians, despite interstate hostility
In the 2017 wave of CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey, 40% of the population of Georgia named Russia as the main enemy of the country. Turkey and the United States garnered the second highest share of responses with 3% each. Yet, no particular animosity towards ethnic Russians is observed in answers to a question about people’s (dis)approval of individuals of their ethnicity doing business with Russians. This blog post examines how answers differ by people’s opinions about whether or not Russia is the main enemy of Georgia.Which groups name Russia as Georgia’s main enemy?
In 2017, 40% of the population of Georgia named Russia as the main enemy of Georgia. Yet the opinion that Russia is the main enemy of the country is not equally present in different demographic groups. This blog post uses data from CRRC’s 2017 Caucasus Barometer survey to gain a better understanding of the characteristics of those who report Russia is the country’s main enemy.Disinformation in the Georgian media: Different assessments for different media sources
In Georgia, supporters of the government and opposition often express contrasting opinions about the independence and reliability of specific news outlets. Based on the CRRC/NDI December, 2017 survey findings, this blog post looks at whether people think or not that the Georgian media spreads disinformation, which groups tend to think so, and how this opinion differs by type of media. “Disinformation” was defined in the questionnaire as “false information which is spread deliberately with the purpose to mislead and deceive people,” and the questions about it were asked separately about TV stations, online media, and print media.The EU, USA or Russia: Who is believed to be able to support Georgia best?
In recent years, Georgia has benefited from EU and US assistance, with around €400 million indicatively allocated for the EU’s projects in Georgia in 2017-2020, and the US government increasing assistance to Georgia in the 2018 Spending Bill. In contrast, Georgia’s relationships with Russia are tense, with diplomatic relations terminated in 2008.Who doesn’t want democracy for Georgia?
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Georgia adopted western-style democratic institutions. They have never functioned in a fully democratic manner, fluctuating between more liberal and authoritarian tendencies. That is, Georgia is and has been a hybrid regime.But what do people want?
Does our algorithm still work?
Within the Russian Propaganda Barometer Project, funded by USAID through EWMI’s ACCESS program, CRRC-Georgia created a model, using a k-nearest neighbors algorithm, which attempts to predict whether a person falls into one of three groups: consistently pro-Western; anti-Western; or neither and potentially at-risk of being influenced towards an anti-Western foreign policy position. The model used data from NDI and CRRC’s polling between 2008 and July 2018. It included variables for age, education level, settlement type, and when the survey was conducted.It’s the economy stupid: An experiment on Georgian support for the European Union
Georgians are enthusiastic in supporting the country’s accession to the European Union. Since 2012, when the National Democratic Institute (NDI) and CRRC-Georgia started tracking attitudes, three quarters of Georgians approved of the government’s goal of joining the EU, on average. What motivates Georgians to support the Union, or alternatively, to abandon support? A survey experiment included in the latest CRRC/NDI poll suggests potential economic burdens have a modest yet significant effect on support for membership. Results do not support the common belief that a potential military threat from Russia dampens Georgians’ support for the EU.
Analysis | Who is afraid of the Lugar Centre?
CRRC-Georgia investigates who is more susceptible to Russian-pushed conspiracies surrounding Georgia’s US-funded Lugar Centre.
In Georgia, a conspiracy about the US-funded Richard Lugar Centre for Public Health Research in Tbilisi has recently gained traction. As CRRC-Georgia’s USAID-funded research shows, Georgia’s far-right groups eagerly picked up on this conspiracy and blamed the centre for the seasonal flu outbreak in early 2019.
The direction Georgia’s headed in
The most recent NDI polling showed a decline in the direction the country was heading. Though not the direct cause by any means, the growing sense that Georgia is going in the wrong direction was likely an enabling factor for the protests that erupted in June and have continued through July in Tbilisi. The CRRC-NDI survey has tracked the direction people think the country is headed over the last decade. While numerous factors affect people’s perceptions of where the country is going, a number of events including elections and the devaluation of the Georgian Lari against the US Dollar appear to show up in CRRC-Georgia and the National Democratic Institute’s data. This blog provides an overview of how views of the direction the country is headed in have changed over time.Perceived Threats to Georgia’s Security
Russian aggression is a key security issue for Georgia. In August 2008, a war broke out over the South Ossetia region with Russia party to the war. Since the war, there have been attempts to restore economic and diplomatic relations between the two countries. Some in Georgia support a policy of having closer ties with Russia. Still, the April CRRC/NDI 2019 survey shows that the public continues to see Russia as a threat.Attitudes toward politicians are related to evaluations of institutional performance
How citizens evaluate the performance of the state is often a reasonable proxy for its performance. In Georgia, evaluations of public institutions are mixed. While a number of social and demographic variables are associated with people’s perceptions of state performance, so too are people’s attitudes towards political parties and politicians. This shows once again how politics is personalized in Georgia.What divides and what unites Georgian society?
The last year has seen a number of conversations about polarization in Georgia. The President of the European Council, Donald Tusk, even commented on the issue in his Batumi speech. One of the components of polarization, though not the sole factor, is division in society over actors, issues, and institutions.While many things could divide the public, what do the people think and which groups report more and fewer sources of division? The April 2019 NDI-CRRC poll suggests that there are fewer perceived reasons for division in rural areas and among ethnic minorities.
Young people are learning English in Georgia
A common sentiment when discussing foreign languages in Georgia is that young people know some English, older people know Russian, and those in between are mixed. Previous CRRC Georgia analysis from 2014 supported this claim, showing that knowledge of English was on the rise among young people.The 2019 survey on Knowledge and Attitudes towards the European Union in Georgia which CRRC Georgia carried out for Europe Foundation suggests that this trend is continuing in Georgia.
Government employees assess the work of the government better than the general public
The outlook in Georgia continues to be increasingly pessimistic, with more people reporting that the country is heading in the wrong direction. Similarly, performance assessments of government institutions have been on the decline in recent years. As recent CRRC analyses have highlighted, party identification, attitudes towards individual politicians, ethnicity, and Georgian language proficiency among ethnic minorities are associated with attitudes towards government. Analysis of the July 2019 CRRC and NDI survey suggests that working for the state is also associated with performance assessments. However, government employees in poor households and those in Tbilisi rate government performance significantly worse.Georgia’s Foreign Policy Trilemma: Balance, Bandwagon, or Hedge? Part 1
Georgia is a small, partly free democracy in a tough neighbourhood, and NATO membership remains an unfulfilled promise. While Russia is widely perceived as the main threat to Georgia’s security, the appropriate strategic or political response to the threat is not obvious. What options does Georgia have when faced with a powerful rival on its border, and what public support is there for these options?Georgia’s Foreign Policy Trilemma: Balance, Bandwagon, or Hedge? Part 2
The first part of this blog post discussed evidence of an association between perceiving Russia as the main threat to Georgia and a preference for a foreign policy that balances against that threat through alliances with the West. The relationship between threat perception and hedging, defined as attempting to maintain good relations with both Russia and the West, is less clear.In a sea of pessimism, who is optimistic about Georgia?
The CRRC and NDI survey released two weeks ago showed a pessimistic picture – half the public thinks Georgia is going in the wrong direction, 24% that nothing is changing, and only 19% think it is going in the right direction. A majority (59%) think the country is not a democracy for the first time since the question was asked on the survey in 2010. Moreover, performance assessments of government, parliament, the courts, and most ministries declined.What kind of electoral system do Georgians actually want?
On 8 March, Georgia’s political leaders agreed on a new electoral system under which 120 seats will be allocated via proportional elections and 30 seats will be allocated via direct election of candidates.The long-fought-over electoral reform was a compromise which represents two steps forward after three steps had been taken back.
As COVID-19 sends political campaigning to Facebook, will polarisation increase?
With Georgia in an election year and traditional face-to-face campaigning out of the question given the COVID-19 outbreak, the importance of Facebook in Georgian politics is only likely to grow.Facebook is an important part of Georgian politics. Political campaigns are fought, and public opinion thought to often be formed on the platform...
AI and Russian propaganda: it’s not what it looks like
In the think tank world, talk about artificial intelligence (AI) is common. Using it is less common. One of the underlying causes of this may be a perceived lack of familiarity with the methods. However, AI methods – including machine learning – are probably more familiar to many thinktankers than they realise. The Russian Propaganda Barometer project, recently conducted by the Caucasus Research Resource Centers (CRRC) Georgia, demonstrates the potential of these tools in think tanks for policy insight – particularly relating to discourse analysis, and developing targeting strategies.Is Georgia really polarised?
Talk about political polarisation in Georgia is easy to find. Some have suggested that the recent United National Movement (UNM) announcement that Saakashvili will be their prime ministerial candidate will only make matters worse.
A new data analysis CRRC Georgia released on Tuesday suggests that this may in fact be the case. Data from several years of CRRC Georgia and NDI polling indicates that there are few ideological or policy issues that the supporters of Georgian Dream (GD) and the United National Movement (UNM) disagree about. Rather, attitudes towards politicians and political events are what divides, a fact the public intuitively recognises.
Georgian voters: personalities, policies, or a bit of both?
While personality in politics matters greatly for the Georgian public, data from this year shows that for Georgian Dream and United National Movement voters, policy is still important.
A recent CRRC Georgia policy brief argued that what was really dividing Georgians politically was personalities rather than policies. Data from the August 2020 CRRC and NDI survey provides further evidence for this idea.
However, the data also shows a difference between Georgian Dream (GD) and United National Movement (UNM) voters in terms of policy preferences and that economic policy is the most important issue for a plurality of voters.
UNM supporters are especially pessimistic about their economic future
With the pandemic still raging and accompanying economic restrictions still in force, Georgians are unsurprisingly pessimistic about their economic future. This holds true especially for supporters of the opposition United National Movement Party, above all other party supporters.
COVID-19 restrictions have impacted people’s economic activity heavily. This is reflected in key economic indicators such as GDP, which declined by 5.9% year on year between January and November 2020.
It is also reflected in employment, with fewer people reporting starting new jobs and more people reporting having lost one, according to the 2020 Caucasus Barometer.
Грузини хочуть, щоби їхній уряд підтримав Україну
Війна Росії з Україною шокувала світ. Вона також шокувала Грузію, а нове опитування від CRRC Georgia викриває ступінь наявних політичних наслідків.
Наслідки війни, що стосуються зовнішньої та внутрішньої політики Грузії, виявилися доволі масштабними. Офіційна позиція Грузії щодо війни була суперечливою: в той час як прем’єр-міністр Іраклі Гарібашвілі категорично заявив, що Грузія не приєднається до санкцій, накладених Заходом проти Росії, президент Грузії Саломе Зурабішвілі почала медійний та дипломатичний бліц у Європі, висловлюючи рішучу підтримку Україні.
How do Georgians feel about the influx of Russians?
Recent CRRC data shows that a large majority of the Georgian public is concerned about the migration of Russians to Georgia.Since Russia launched its invasion of Ukraine in February 2022, at least 1.2 million Russian citizens have entered Georgia, equivalent to roughly 30% of Georgia’s population. While the number of Russian citizens who have decided to stay in Georgia remains unclear, the impact of this mass migration is strongly felt in rising rents and concerns over the country’s security.
Is the Georgian government doing enough to secure EU membership?
CRRC Georgia data suggests that while the majority of Georgians want to join the EU, they are largely split along partisan lines on whether their government is doing enough to secure the country’s candidate status.Is People’s Power designed to make Georgian Dream look good?
A CRRC Georgia study found that positioning Georgian Dream as more moderate than its spin-off group, People’s Power, increased support for the ruling party.A popular study suggests that when a person goes for a date, they will be more liked if they take a similar, but slightly less attractive companion with them. Likewise, political parties often look better for their voters when they position themselves against a similar, but less appealing opponent.
რა სარგებლობა მოაქვს ხალხის ძალას მმართველი პარტიისათვის?
CRRC Georgia-ს კვლევამ აჩვენა, რომ ქართული ოცნების უფრო ზომიერად პოზიციონირებამ, ვიდრე მისი სპინ-ოფ ჯგუფი ხალხის ძალაა, მმართველი პარტიის მხარდაჭერა გაზარდა.Are individual Georgians politically polarised?
CRRC-Georgia data found that individual political polarisation — how committedly partisan a person is — is relatively low in Georgia, despite concerns about the country’s polarisation as a whole.What do the ‘tragic consequences’ of colour revolutions actually look like?
While Russia regularly warns against the supposed negative consequences of ‘colour revolutions’, data from the Varieties of Democracy project suggests that anti-regime protests leading to changes of government in former Soviet countries have led to lower corruption, cleaner elections, and more vibrant civil society.Georgians’ attitudes and beliefs associated with polarised media preferences
A recent NDI/CRRC survey suggests that Georgians have markedly different beliefs about the present state and future of their country, regardless of their party sympathies, depending on whether the television channel they trust is pro-government or pro-opposition.Do Georgians feel like they are being spied on by the government?
Nearly half of the Georgian public think that they or their family members are under government surveillance at least some of the time.Georgia’s changing priorities at the UN General Assembly
A quantitative analysis of the speeches made by Georgia’s leaders at the annual UN General Assembly found that their themes and priorities changed after the change of government in 2012, with Georgian Dream leaders more positive and discussing Russia less negatively than their predecessors.Russian émigrés in Georgia
After the beginning of Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine, tens of thousands of Russian nationals moved to Georgia, with many choosing to stay. A CRRC survey found that Russian respondents in Georgia believe that Russia is not a democracy, have mixed views about Georgia’s political direction, and feel relatively secure in Georgia.Can political parties in Georgia survive abandonment by their leaders?
A year before Georgia’s general elections, a CRRC survey found that less than half of surveyed Georgian partisans would remain loyal to their favoured party if its leader were to establish a new party, with supporters of the ruling party more likely to stick with their party than supporters of the opposition.