Obstacles to accessing Georgia’s courts
Note: This article first appeared on the Caucasus Data Blog, a joint effort of CRRC-Georgia and OC Media. It was written by Salome Dolidze, a Researcher at CRRC-Georgia. The views presented in the article are the author’s alone and do not necessarily represent the views of CRRC-Georgia, Caucasian House, or any related entity.
A CRRC Georgia survey investigated who considers and who pursues litigation in Georgia, and the obstacles people face in doing so.
Georgia’s court system faces significant issues, with reports suggesting that long delays, access to the legal system, and overloaded caseloads are among the barriers that prevent citizens from using the courts.
A 2021 Social Justice Center report noted that geography, the physical accessibility of buildings, a lack of legal awareness and empowerment, and other physical, financial, cultural, and social barriers presented challenges for large segments of Georgian society. A recent CRRC Georgia survey looks specifically at who goes to court and who considers it, but ultimately doesn’t, and the challenges both groups face in their pursuit of justice.
Overall, 4% of those surveyed reported they went to the courts over the six years prior to the survey, and a further 4% reported that they considered starting litigation but decided not to. Among those who went to court, 71% were there for civil litigation, 17% for criminal cases, and 12% for administrative legal disputes.
The data suggest there are a number of differences between social and demographic groups in terms of who goes to court.
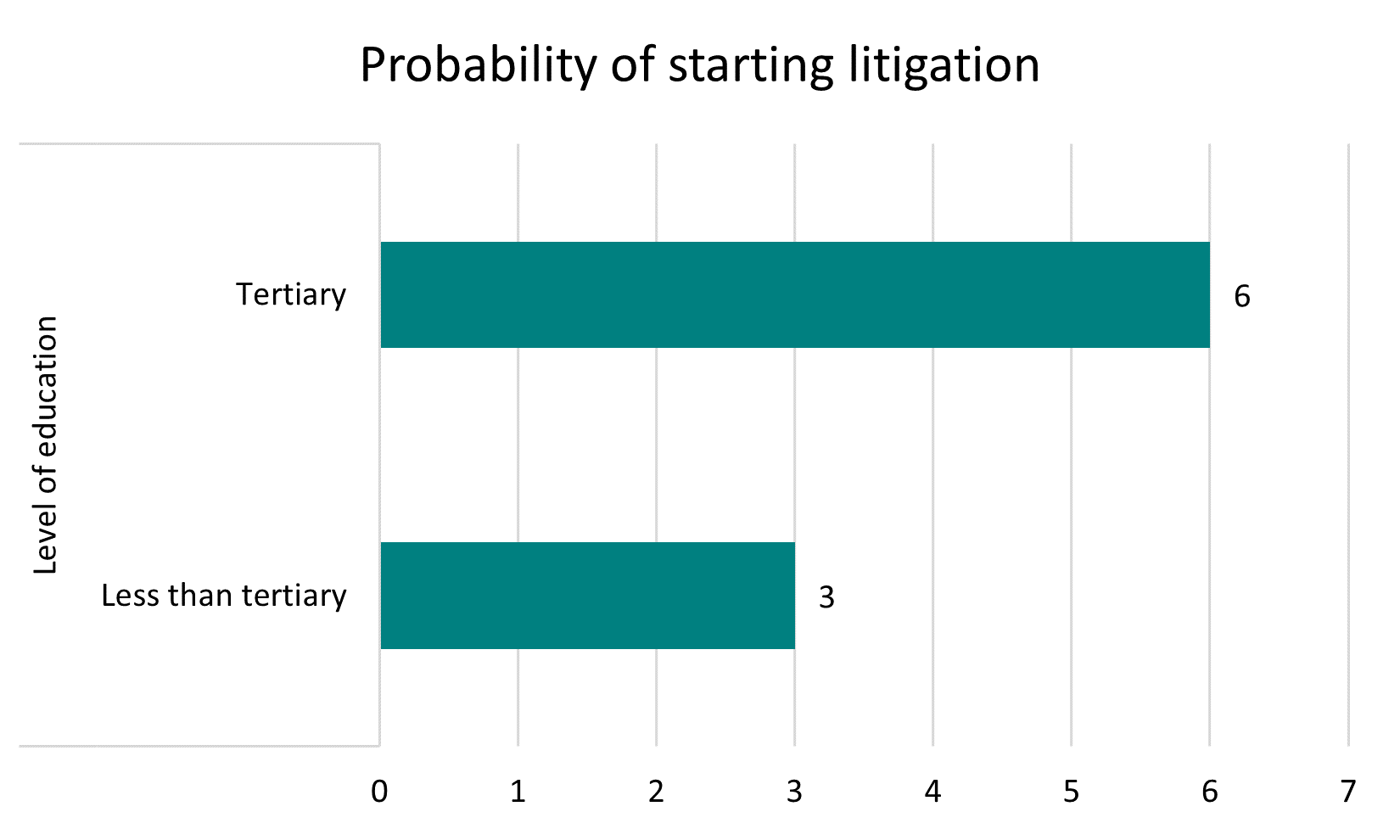
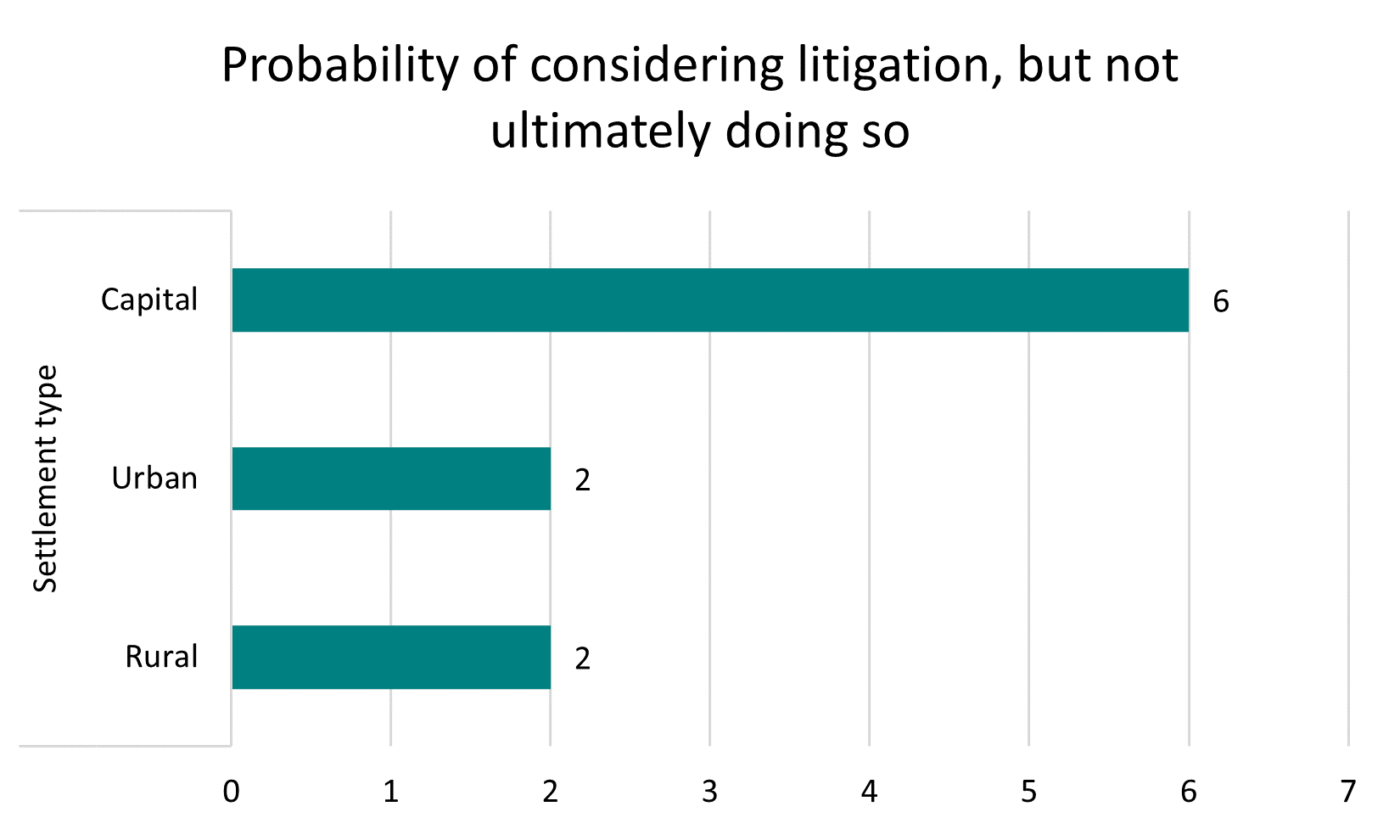
Those who had tertiary education were more likely to have started litigation than those without. People living in urban areas outside of Tbilisi were more likely to have considered starting litigation, but ultimately refrained from doing so, than those living in the capital.
Other social and demographic variables such as sex, ethnicity, employment status and wealth were not associated with whether or not someone considered starting litigation or actually did so.
The data also provided insight into the main challenges people faced in Georgia’s court system, as well as the reasons why people ultimately decided not to use the courts.
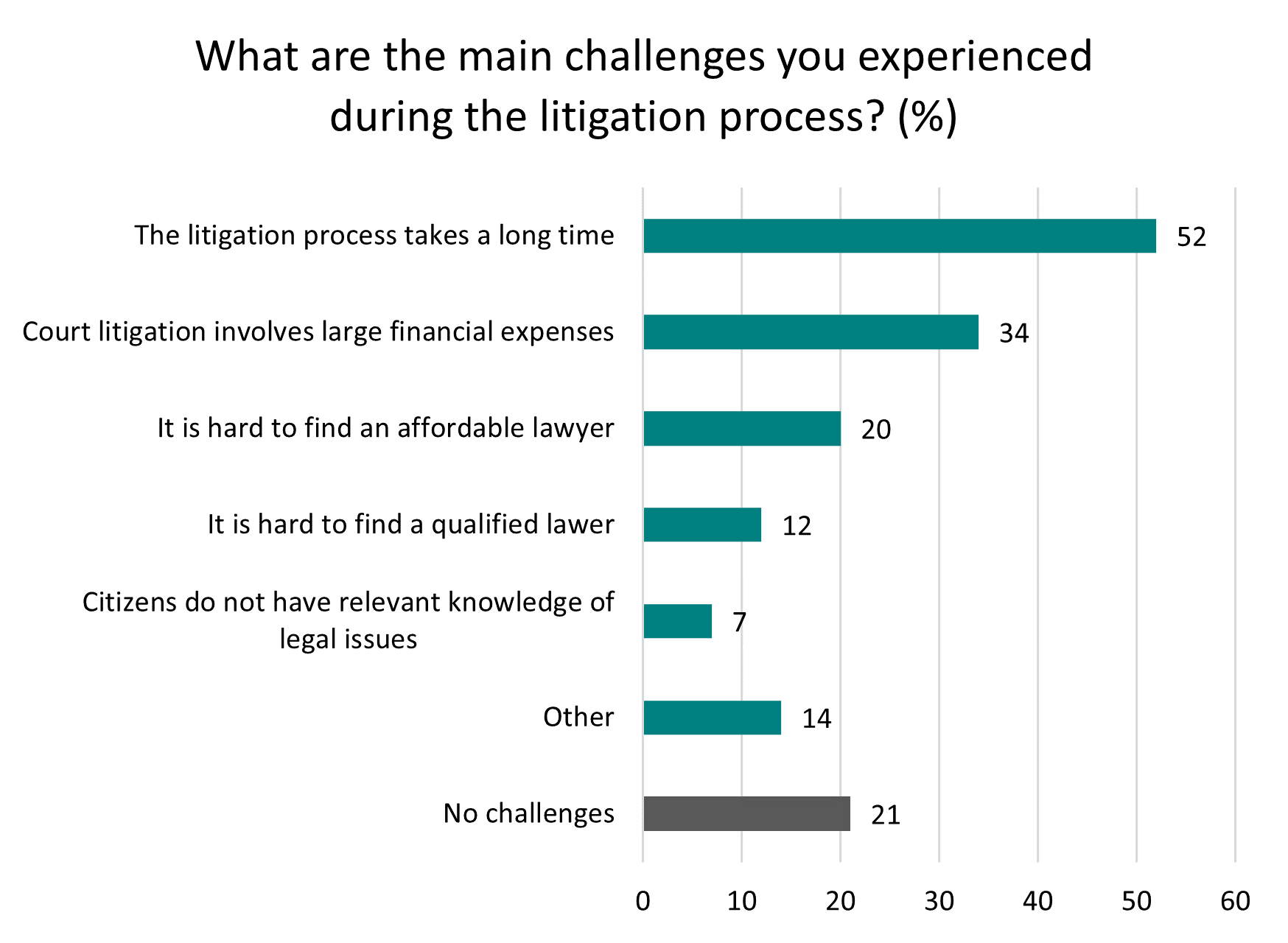
When people who had actually engaged in litigation were asked about difficulties they had encountered during that process, a majority of respondents (52%) stated that the litigation process takes too long. Another significant concern was the cost associated with litigation, which was cited by 34% of respondents that went to court. In addition, 20% highlighted the difficulty of finding an affordable lawyer, with another 12% stating that finding a qualified lawyer was a challenge. Legal expertise can, of course, be critical to navigate the complexities of the legal system, and ensuring a fair and just outcome.
The lack of legal expertise amongst ordinary citizens (7%) was highlighted infrequently. Approximately one fifth of respondents (21%) mentioned that they encountered no difficulties in the litigation process.
When respondents who had considered starting litigation, but not done so were asked why they had chosen not to go to court, a number of key factors stood out.
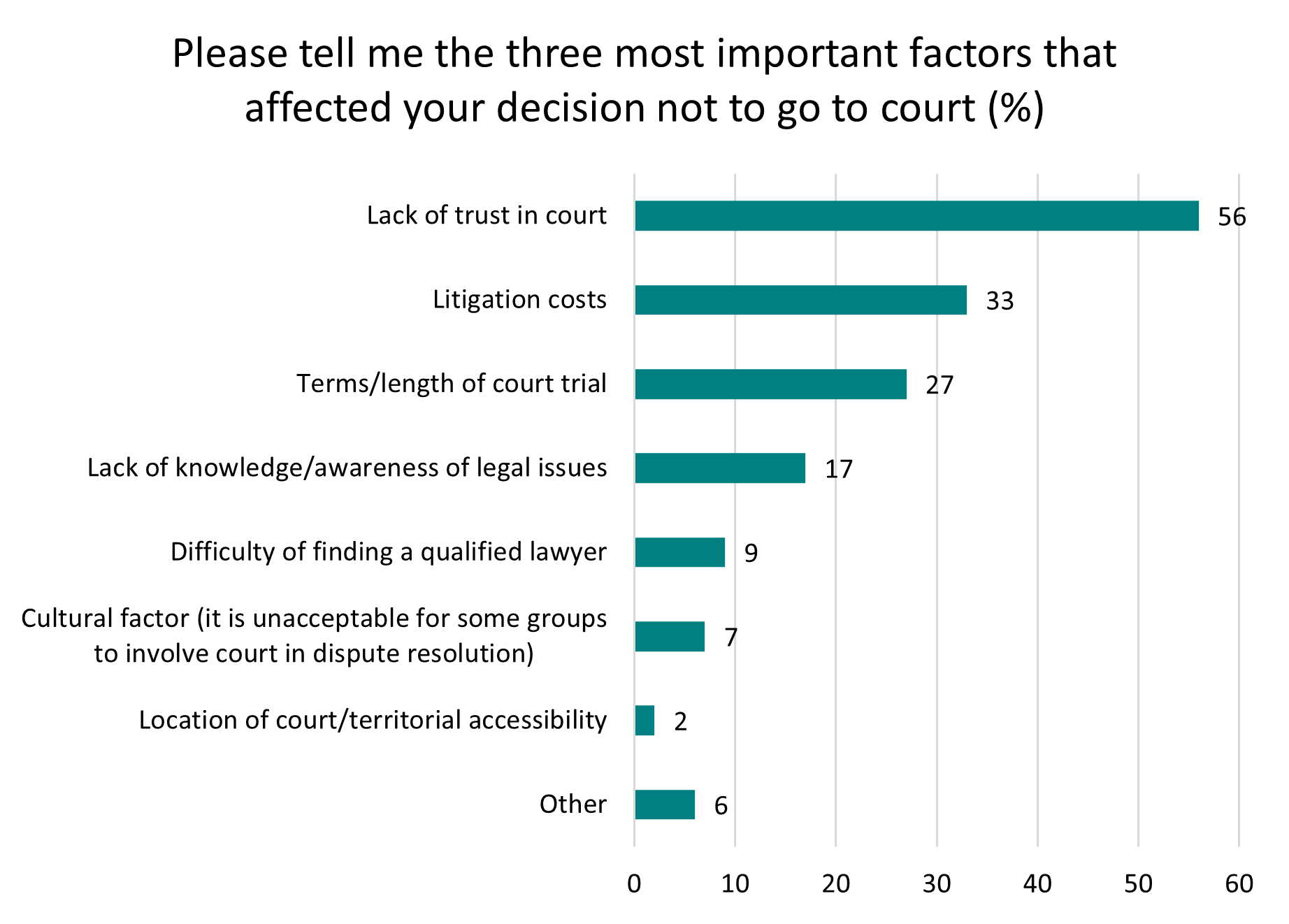
A lack of trust in the judicial system was the most commonly given reason, with 56% of respondents identifying this as a significant deterrent. Another prominent concern for those who refrained from legal action was the cost of litigation, mentioned by 33% of respondents. The length of court trials was also cited by 27% of those who ultimately chose not to pursue litigation. Other significant concerns included lacking knowledge or awareness of legal matters (17%).
One in twenty Georgians have considered going to court in the last six years, and a further one in twenty went to court. Among those who went to court, prolonged court procedures, financial constraints, and a lack of trust in the judicial system were cited as significant barriers to accessing justice in Georgia.
The data used in this article is available here. The regression analysis used in this article included the following variables: Age (18-34, 35-54, 55+); Sex (male or female); Settlement type (Tbilisi, other urban, rural); Education level (tertiary or not); Ethnicity (Ethnic Georgian or ethnic minority); Employment status (employed or not working); Wealth index (A simple additive index of ownership of a number of durable goods within a household).