Does Georgia’s public want gender-balanced politics?
CRRC Georgia surveyed the Georgian public on attitudes towards gender equality in politics and obstacles faced by women in politics in Georgia.
Gender equality in politics is an important issue globally, and Georgian policy on the issue has been developing in recent years. Georgia introduced mandatory gender quotas for proportional party lists in 2020, extending this provision until 2032. The legislation stipulates that at least one out of four candidates submitted to the Central Election Commission, and provides financial support to parties that nominate more women.
Despite these policy changes, much remains to be done to ensure gender equality in practice. In the 2020 parliamentary elections, only three political parties and one electoral bloc benefited from the financial incentive mechanism for nominating more female candidates than the mandatory gender quotas required. A study on mandatory gender quotas in Georgia found that in 2022, women still made up only 19% of Georgia’s parliament.
Harassment directed at politicians is also a significant barrier. A CRRC study found that female politicians in Georgia more frequently faced online violence (abusive and harassing comments) related to their personal life than male candidates and politicians, in the two months before the 2020 parliamentary elections.
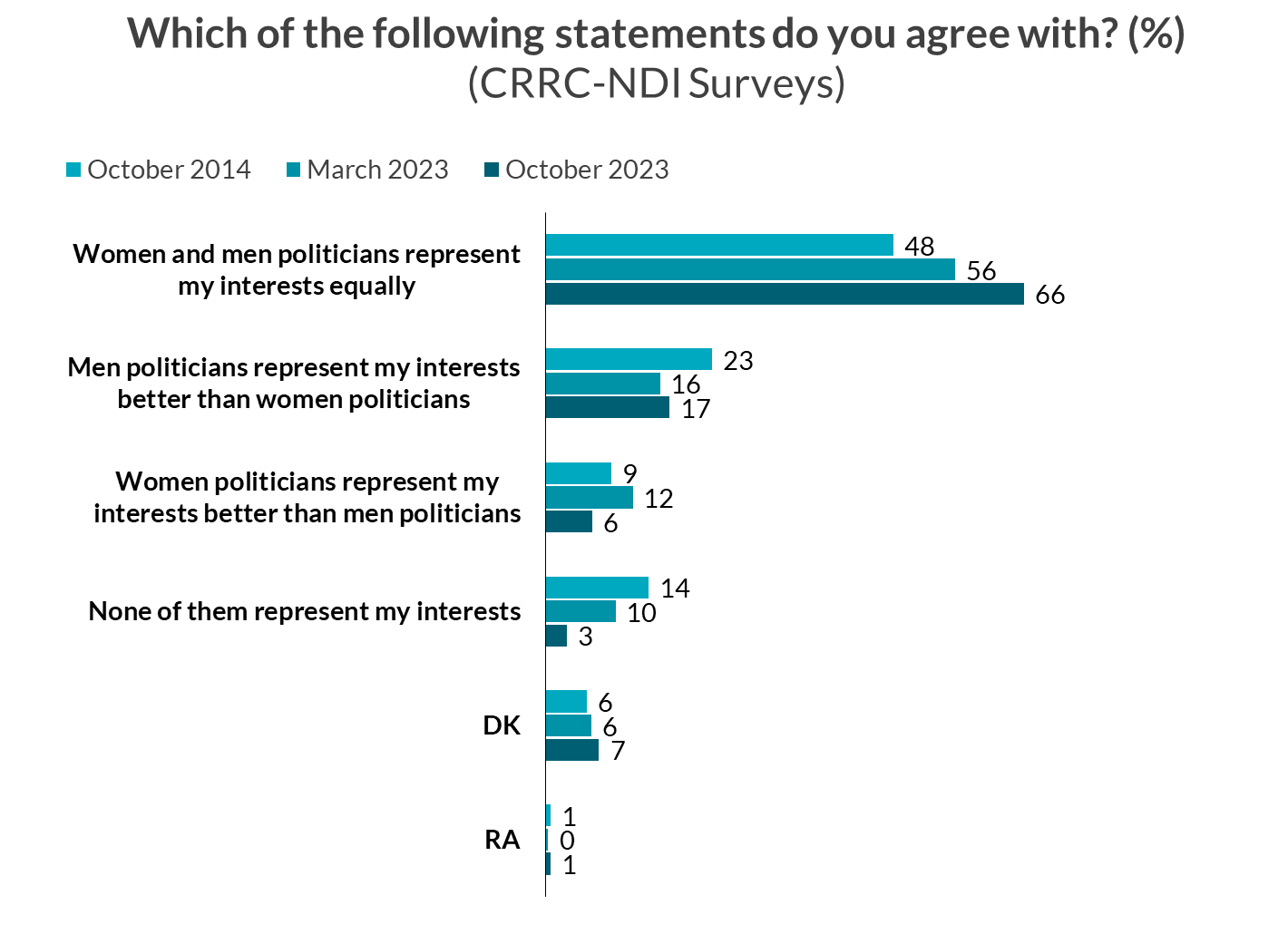
Despite those challenges, data from the NDI and CRRC October 2023 survey suggest that the public’s attitudes are becoming more approving of gender equality in politics.
Two thirds of those surveyed believed that female and male politicians represented their interests equally. This marked a 10 percentage point increase compared to March 2023, and an 18 point increase compared with October 2014, when CRRC first asked the survey question.
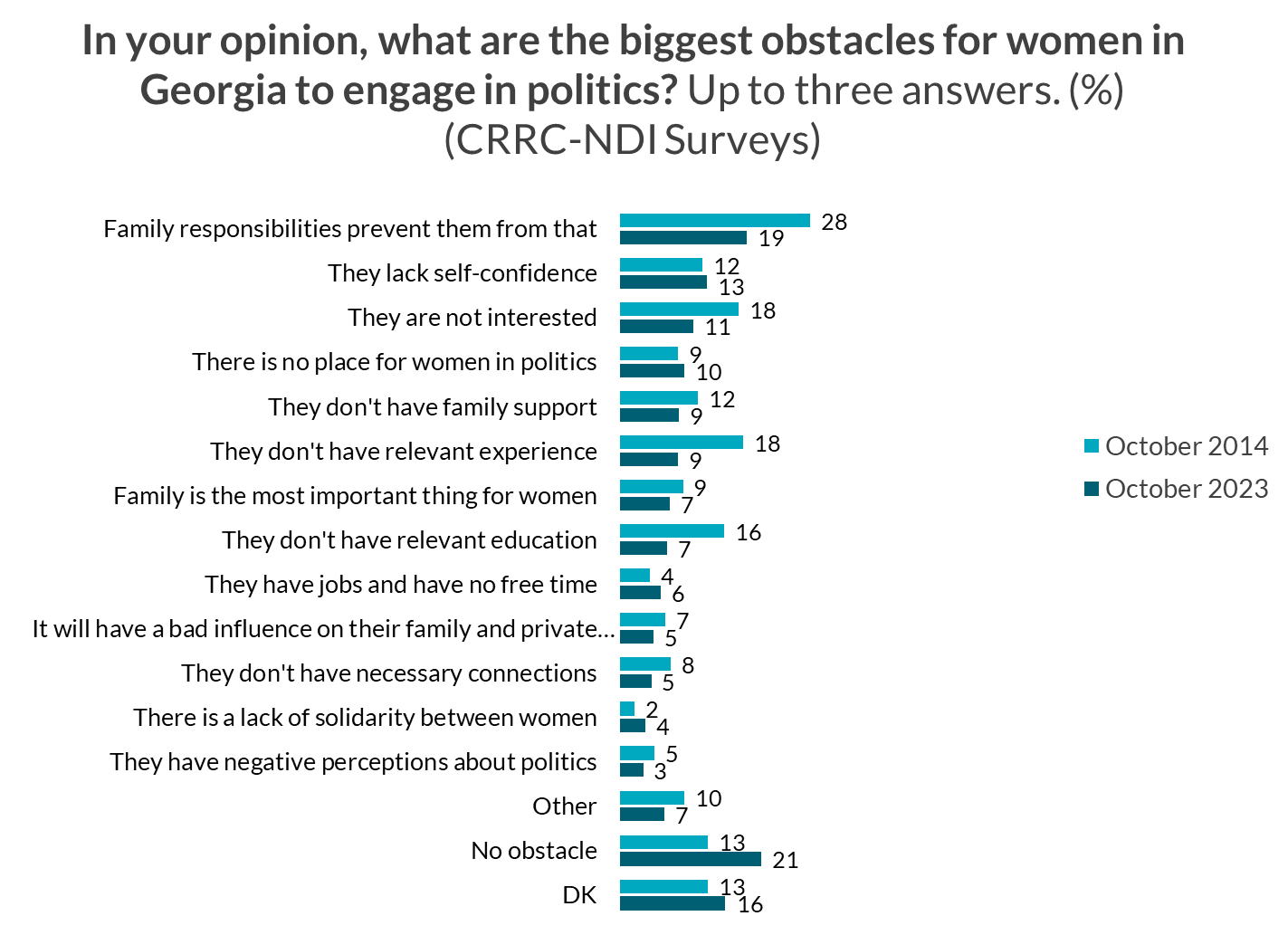
The survey also asked respondents what they believed were the largest obstacles preventing women in Georgia from engaging in politics. Respondents were allowed to name up to three issues.
The most frequently named obstacles were family responsibilities (19%), a lack of self-confidence (13%), and women having no interest in politics (11%). One in ten (10%) reported the perception in the public that there was no place for women in politics was an obstacle, and 9% believed women were hindered by a lack of family support.
However, these attitudes have also changed in the past decade. There was a nine percentage point drop in the share of those who named family responsibilities as an obstacle compared to 2014. The share reporting that women had a lack of interest in politics also decreased by seven percentage points. The percentage of respondents who named a lack of relevant experience and education halved, moving from 16% to 7% and 18% to 9%, respectively.
However, there was also a seven percentage point increase in the share of respondents who stated that women face no barriers to engagement in politics since 2014.
The above data shows substantial progress toward greater acceptance of gender equality in politics.
Despite the belief that some issues, such as family responsibilities and a lack of self-confidence, remain barriers preventing women from entering politics, the decreasing percentage of respondents citing these as obstacles suggests a changing landscape in the country.
This article was written by Elene Ergeshidze, a Researcher at CRRC Georgia. The views expressed in the article are the author’s alone, and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Democratic Institute, CRRC Georgia, or any related entity.