Number of logical inconsistencies in 2016 election protocols decline
Following the 2016 parliamentary elections, a number of politicians questioned the results based on logical inconsistencies on election protocols. Some of the election protocols, which summarize election results for individual voting stations, reported that more voters had come to the polls than actually cast ballots while others reported that more votes had been cast than voters came to the polling station. While both did happen, the Central Election Commission has made dramatic improvements compared to Georgia’s 2012 parliamentary elections.
In the 2012 parliamentary elections, according to an analysis of data the Central Election Commission provided, in the proportional list elections alone there were over 30,000 more voters that came to the polls than cast ballots. In 2016, there were less than 3000 such voters – a clear improvement.
Not only were there more voters than votes in many precincts – there were more votes cast than voters that came to the polls, again according to the official record. In the 2012 parliamentary elections, there were 696 more votes than signatures for those votes. By comparison, in 2016 there were 76 – again a clear improvement.
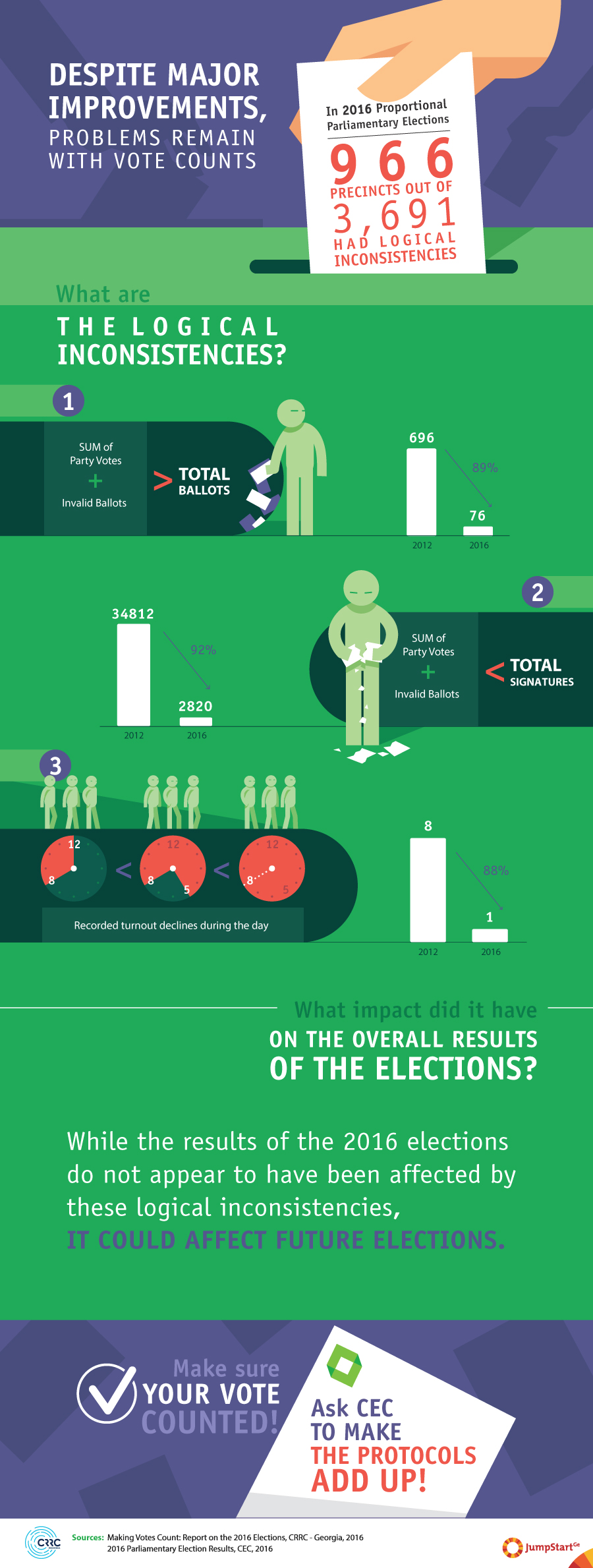
A third logical inconsistency present in the data is declining turnout. In the 2012 elections, in 8 precincts, there were more votes at 12PM than at 5PM. That is to say that the precincts recorded declining turnout. In 2016, by contrast, only one precinct reported declining turnout, again, a clear improvement.
While the CEC has clearly improved its recording of the vote in 2016, and small mismatches are bound to happen, any voter may reasonably ask themselves – if the CEC cannot make election protocols add up, how do I know my vote counted? Thus, we strongly recommend that the CEC make efforts to minimize the number of logical inconsistencies in future elections. Some recommendations on how the CEC might do so are available in our report on the 2016 elections.
Note: The DEFDA project is funded by the Embassy of the United States of America in Georgia, however, none of the views expressed in the above blog post represent the views of the US Embassy in Georgia or any related US Government entity.
Before and After the Elections: Shifting Public Opinion in Georgia
Electoral Notes- Municipal Elections, 2014
Trust in local government in Georgia
Making Votes Count: Statistical Anomalies in Election Statistics
Direct observation of polling stations is the best method available to ensure the accuracy of the vote, however, election observers cannot be everywhere all the time. Given this fact, the field of election forensics, a subfield of political science, has developed a number of statistical tests to look for statistical anomalies in election returns, which may suggest suspicious election-related activity.Making energy matters matter: entering the electoral field
Democracy in Georgia
Rule of Law in Georgia - Opinions and Attitudes of the Population
Election Day Portal
Testing Mobile Innovation in our Surveys
SMS Survey | First Insights
Election Maps | Who Did Your Neighbors Vote For?
CRRC's Media-Monitoring Project: TV Coverage of the Election Campaigns
Analysis of Preliminary Election Results
In order to help monitor the fidelity of the October 2016 parliamentary election results, CRRC-Georgia has carried out quantitative analysis of election-related statistics within the auspices of the Detecting Election Fraud through Data Analysis (DEFDA) project. Within the project we used methods from the field of election forensics. Election forensics is a field in political science that attempts to identify Election Day issues through looking at statistical patterns in election returns. This blog post reports the results of our analysis.USAID Political Party Assessment of Europe and Eurasia
Exit Polls | Take Two
Parliamentary Elections in Georgia | ODIHR Observation
Georgian Election | ODIHR Preliminary Report and its Percentages
Georgia post-Election Phone Survey | Quick Review
PFA Report on “Armenia’s 2008 Presidential Election”
McCain vs Obama: Caucasus preferences
Freedom House Report | Democracy in the Caucasus
Caucasus Election Programs in the 1990s
Exit Polls | a good idea?
With upcoming elections in Georgia, the attention is back on a theme that otherwise often gets neglected: what does the Georgian electorate want?Electoral forensics on the 2016 parliamentary elections
In order to help monitor the fidelity of the October 2016 parliamentary election results, CRRC-Georgia has carried out quantitative analysis of election-related statistics within the auspices of the Detecting Election Fraud through Data Analysis (DEFDA) project.Three months before the 2016 Parliamentary elections: Trust in the Central Election Commission and election observers in Georgia
The June 2016 CRRC/NDI Public attitudes in Georgia survey, conducted three months before the Parliamentary elections, provides interesting information about trust in the Central Election Commission (CEC) and election observers, both local and international.Gender (in)equality on TV
Stereotypes are an inseparable part of every society, and present in many parts of everyday life. Georgian society is no exception in this regard. For example, some professions like teaching are stereotypically thought of as “women’s professions” while others like being a soldier are considered “men’s professions”. The media is considered one of the strongest means through which stereotypes are strengthened or broken. In Georgia, TV is the most important media, given that according to CRRC/NDI data, 73% of the population of the country name television as their primary source of the information. In order to understand the dynamics around gender-based stereotypes on TV, CRRC-Georgia monitored the main evening news releases and political talk shows broadcast during prime time (from 18:00 to 00:00) on five national and three regional channels from September 11 to November 12, 2017 (Channel One of the Public Broadcaster, Adjara, Rustavi 2, Imedi, Maestro, Trialeti, Gurjaani, Odishi) with the support of the UN Joint Program for Gender Equality with support from UNDP Georgia and the Swedish government.საარჩევნო გარემო ეთნიკური უმცირესობებით კომპაქტურად დასახლებულ არეალებში უარესდება
„CRRC საქართველოს“ გამოკითხვის შედეგების მიხედვით, საარჩევნო გარემო ყველაზე მეტად პრობლემატური უმცირესობებით კომპაქტურად დასახლებულ რეგიონებშია და მდგომარეობა უფრო უარესდება.2018 წლის საპრეზიდენტო არჩევნები, განსაკუთრებით კი — მეორე ტურში დატრიალებული მოვლენები შესაძლოა, ქვეყნის დემოკრატიული განვითარების გზაზე უკან გადადგმულ ნაბიჯად ჩაითვალოს. პირველ და მეორე ტურებს შორის მთავრობამ განაცხადა, რომ არჩევნების შემდეგ დაახლოებით 600 ათასამდე მოქალაქეს ვალებს ჩამოაწერდა, რაც, ზოგიერთი დამკვირვებლის აზრით, ამომრჩეველთა მოსყიდვად უნდა ჩათვლილიყო...
What kind of electoral system do Georgians actually want?
On 8 March, Georgia’s political leaders agreed on a new electoral system under which 120 seats will be allocated via proportional elections and 30 seats will be allocated via direct election of candidates.The long-fought-over electoral reform was a compromise which represents two steps forward after three steps had been taken back.
The rallying around the flag effect in Georgia
In times of crisis, support for governments often rises in what is known as a rallying around the flag effect. The COVID-19 crisis in Georgia has been no exception.
Data from around the world has shown rallying around the flag effects in many countries during the pandemic, with a few exceptions. Georgia has followed this broader pattern, with performance ratings tripling for many actors and institutions between November/December 2019 and May 2020.
Georgian voters: personalities, policies, or a bit of both?
While personality in politics matters greatly for the Georgian public, data from this year shows that for Georgian Dream and United National Movement voters, policy is still important.
A recent CRRC Georgia policy brief argued that what was really dividing Georgians politically was personalities rather than policies. Data from the August 2020 CRRC and NDI survey provides further evidence for this idea.
However, the data also shows a difference between Georgian Dream (GD) and United National Movement (UNM) voters in terms of policy preferences and that economic policy is the most important issue for a plurality of voters.
Political campaigning in Georgia: informing or mobilising?
Political campaigning takes a wide range of forms, from digital advertising to door knocking. Generally, campaigning is believed to both mobilise voters to actually go out to vote as well as win over voters, but which is most relevant in Georgia?
Data from the August CRRC Georgia and NDI public opinion poll indicate that people who wanted to be contacted by campaigners also appeared more partisan than others. This may suggest that campaigning in Georgia will be more effective at turning out partisans than persuading the undecided.
Is People’s Power designed to make Georgian Dream look good?
A CRRC Georgia study found that positioning Georgian Dream as more moderate than its spin-off group, People’s Power, increased support for the ruling party.Democratic hypocrisy in Tbilisi
A CRRC Georgia survey found that people living in Tbilisi were more willing to accept democracy-eroding policies if they believed that their preferred party was in power.Can political parties in Georgia survive abandonment by their leaders?
A year before Georgia’s general elections, a CRRC survey found that less than half of surveyed Georgian partisans would remain loyal to their favoured party if its leader were to establish a new party, with supporters of the ruling party more likely to stick with their party than supporters of the opposition.