State capacity in the South Caucasus: How do you measure how much the state can do?
The lack of agreement on indicators and definitions is due to the inherent multidimensionality of the concept. This multidimensionality is well exemplified by Fjelde and De Soya’s 2009 article which identifies state capacity as a state’s ability to coerce, co-opt, and cooperate with society. While the authors provide indicators for these capacities, their schema seems more to describe a state’s relationship and interactions with citizens rather than state capacity in and of itself.
The fact that different scholars have theorized different capacities including fiscal capacity, bureaucratic-administrative capacity, and coercive capacity as component parts of state capacity further illuminates the multidimensionality of the concept. This blog post looks at three of the many possible indicators which could be used to gauge state capacity in the South Caucasus: revenue excluding grants as a share of GDP for fiscal capacity, taxes on income, profit, and capital gains as a share of total revenues for bureaucratic-administrative capacity, and military expenditures as a share of central government expenditures for coercive capacity. So, how strong are the South Caucasus states?
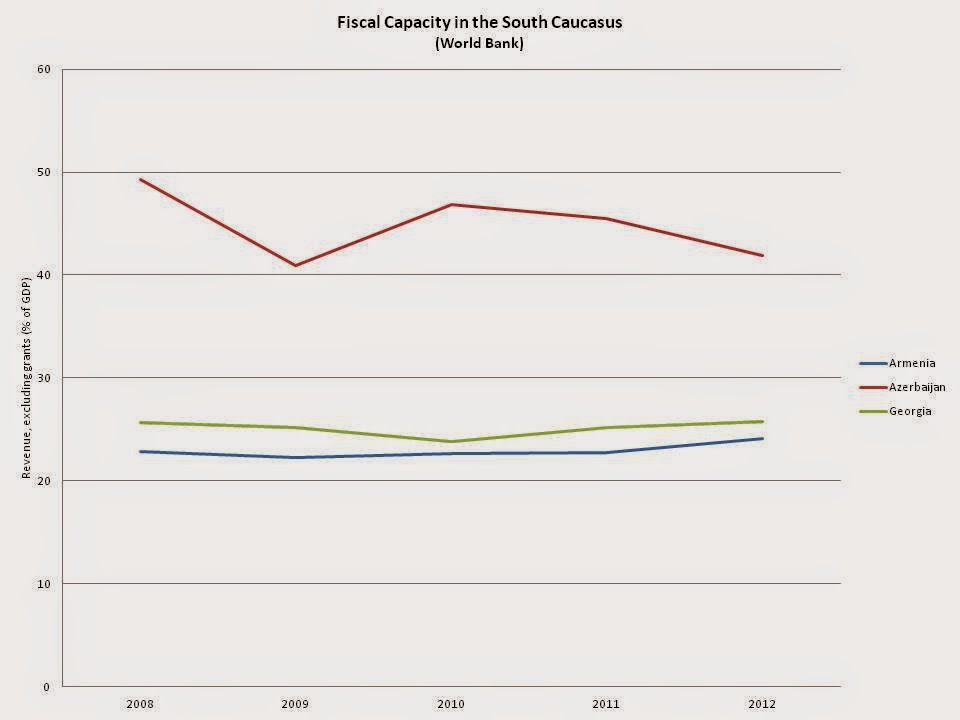
Fiscal capacity is considered one of the most important state capacities by most authors as without the financial means to accomplish a stated policy, that policy will likely never be realized in practice. The graph below presents World Bank data for state revenue excluding grants as a share of GDP and shows how much the South Caucasian governments collect from their societies. What appears most prominently is that Azerbaijan’s fiscal capacity far outstrips that of Georgia and Armenia, which exhibit similar levels of extraction. It is important to keep in mind here that revenue consists not only of taxes but also funds collected through fines, fees, and resource rents. The latter are particularly important for Azerbaijan as the government received 54% and 65% of state revenues from oil and gas in 2005 and 2011 respectively. Without its oil wealth, Azerbaijan would collect significantly less in revenues.
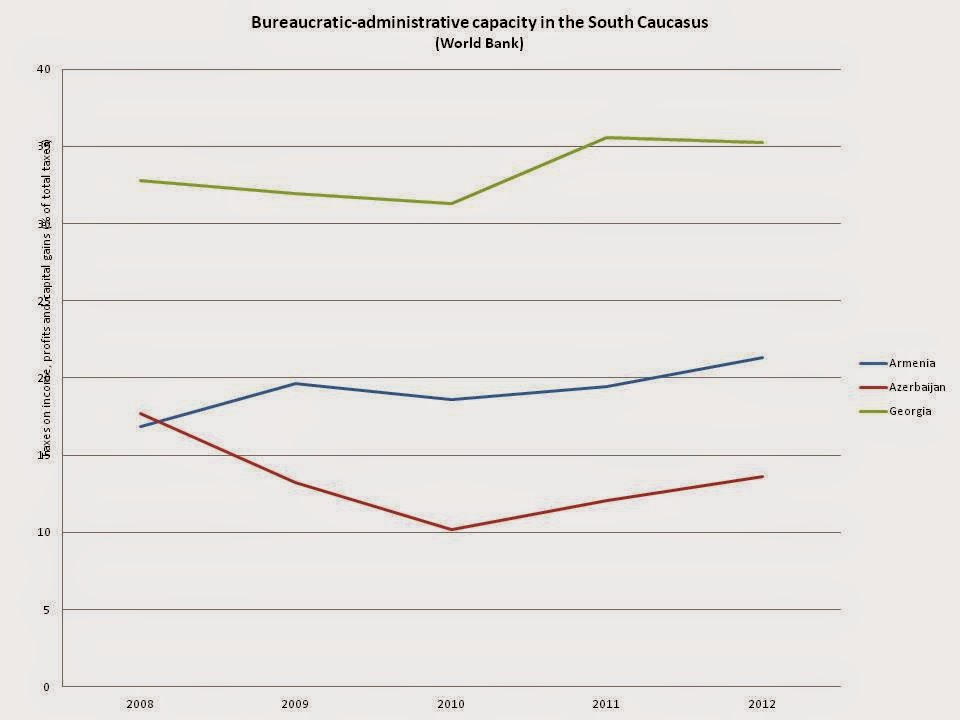
Definitions of bureaucratic-administrative capacity often center on a state’s ability to collect and manage information (Hendrix, 2010). This capacity is central to a state’s ability to act and likely enables a state to have fiscal and coercive capacity. For example, if a state is unable to gather information on potential militants within its territory it will be unlikely that it can coerce or co-opt them into compliance. In order to successfully cooperate with society, information gathered must be channeled into usable and comprehendible forms which enable the government to act.
Income, profit, and capital gains taxes as a share of total taxes are a useful indicator of bureaucratic-administrative capacity. While at first glance it may be taken to indicate fiscal capacity, income taxes are more closely related to bureaucratic-administrative capacity, because this form of taxation is both a relatively difficult and relatively desirable tax to collect (Rogers and Weller, 2014). The desirability of income tax stems from the fact that it generally provides a revenue stream which does not drastically fluctuate. In most circumstances, however, it is a relatively difficult tax to collect (though the system of income tax payment by employers has lowered this difficulty in Georgia, Transparency International Georgia has noted that non-compliance with income tax remains problematic). As such, the share of income tax as a percentage of total state revenues proxies how well a state can extract from and manage information on its population. The graph below presents taxes on income, profits and capital gains (two other taxes which are similar to income tax) as a percentage of total taxes collected. The graph demonstrates that Georgia’s bureaucratic-administrative capacity on this measure is higher than that of Armenia or Azerbaijan. While Azerbaijan’s relative weakness in this sector is likely caused by hydrocarbon revenues, Georgia’s relative strength likely comes from the reforms in tax collection and enforcement, which started with the tax code passed in 2005.
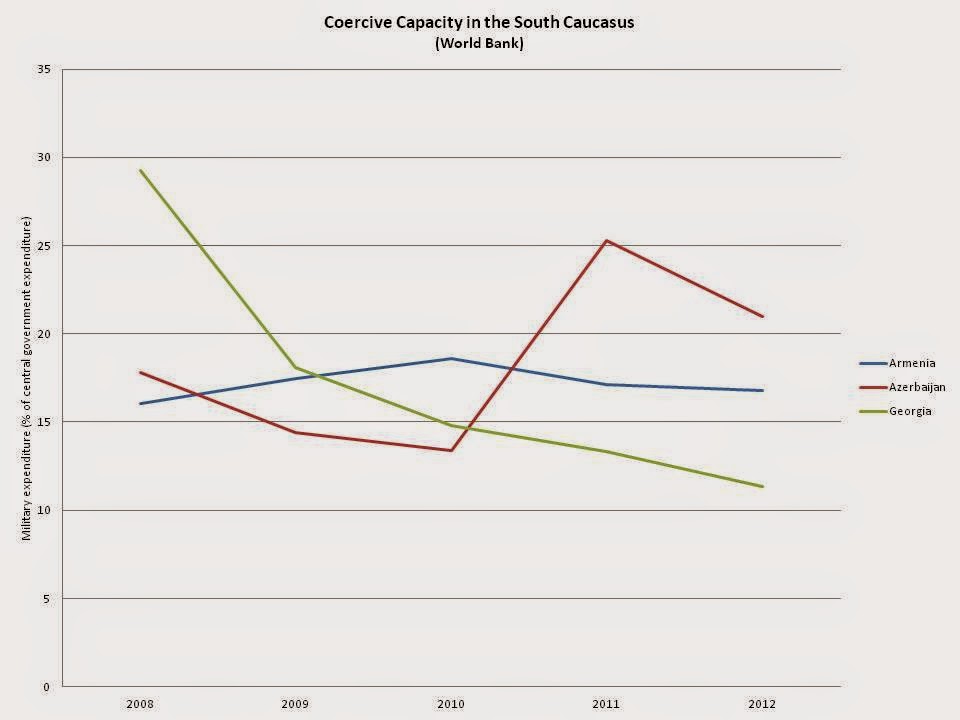
A final important capacity of state is its ability to coerce its population; without the capability to put down paramilitaries or suppress violent groups, a state can quickly devolve into chaos. Taking military expenditures as a share of central government expenditures as an indicator of coercive capacity, the graph below gives a possible indication of coercive capacity. This indicator, though, also likely describes the changing relative importance of coercion to each state over time, as one would expect the share of total expenditures dedicated to military expenditures to increase if security issues became relatively more important – hence Georgia’s relatively high expenditures in 2008, which are largely a result of the 2008 August War with Russia. When looking at the figures, it is important to note that Azerbaijan’s budget is significantly larger than either Georgia’s or Armenia’s and as such has a much larger absolute level of coercive capacity.
This blog post has looked at three of the many possible indicators of state capacity. For readers interested in the subject, this 2010 article by Cullen Hendrix goes through a wide variety of indicators, although the data set used does not include any of the South Caucasus countries.
Have any ideas about other indicators? Join the conversation on Facebook or at CRRC-Georgia’s office on December 10th for the Works-in-Progress talk:State/party capacity and constraints on state action: Operationalizing and indexing state capacity in Georgia and Armenia.
The development of Azerbaijani think tanks and their role in public policy discourse
By Zaur Shiriyev
Think Tanks in Armenia: Who Needs their Thinking?
By Yevgenya Jenny Paturyan
Think tanks are considered to be an important part of civil society: providers and keepers of expertise on important social, economic, environmental, political and other issues. Organizations like Chatham House and Carnegie Endowment for International Peace come to mind. In addition to ‘pure’ think tanks, there is a plethora of organizations that combine research with advocacy and action, Transparency International being a prominent example.
The lay of the land: An interview with Hans Gutbrod on think tanks in the South Caucasus
[Editor's note: This is the second in a series of blog posts co-published with On Think Tanks. The views expressed within this blog series are the authors alone, and do not represent the views of CRRC-Georgia.]Interview by Dustin Gilbreath
Thinking about think tanks in the South Caucasus
By: Dustin Gilbreath
What do CB interviewers’ ratings of respondents’ intelligence tell us?
Citizenship in action in the South Caucasus
Finding work in Armenia and Georgia
CRRC’s third annual Methodological Conference: Transformations in the South Caucasus and its Neighbourhood
Trust in institutions in the South Caucasus – generating a combined score
ქალები საქართველოში და სექსი ქორწინებამდე
Smoking in the South Caucasus and tobacco policy in Azerbaijan
CRRC Methodological Conference on Measuring Social Inequality in the South Caucasus and its Neighborhood
When is a war not a war?
Friends and Enemies in the South Caucasus
In the South Caucasus, the Enemy of my Enemy is my Friend
Perceptions of Court System Fairness in the South Caucasus
Ann Bennett Lockwood, an American attorney, politician and author once said that, “If nations could only depend upon fair and impartial judgments in a world court of law, they would abandon the senseless, savage practice of war”. For many, the credibility of a government is judged by the fairness of itsjudicial system. For instance, Michel Rosenfeld (2001) argued that a fair justice system creates respect and faith in government by saying that, “If a citizen implicitly or explicitly endorses a law or legal regime, the latter can be considered subjectively fair.”The recent history of the South Caucasus as seen by the world’s media – Part 1, Armenia and Azerbaijan
The recent history of the South Caucasus as seen by the world’s media - Part 2, Georgia
Does public opinion accurately gauge government performance in the South Caucasus?
Do Think Tanks in Georgia Lobby for Foreign Powers?
By Till Bruckner
Common challenges, common solutions
By Dustin Gilbreath
Household income and consumption patterns in Georgia
Georgia Corruption Data | Now Available
The Caucasus Barometer 2010 Dataset Is Available!
ODA – CRRC Data Analysis Online
If You Were Asked What Everyone Else Thought of Your Country...
Blood Donation in the South Caucasus: Refill, Please!
Carnegie Research Fellowship Program | Winners Announced
Engagement without recognition?
Is the South Caucasus a homogenous region?
Fancy Living Abroad? 39% of Young Armenians Say "Preferably Forever"
Georgia & Russia | Russian Analytical Digest
Women in Parliament: How Do Georgia, Armenia and Azerbaijan Compare to Other Countries?
Expanding on the topic of a previous blog, this post compares statistics on the number of women in national parliaments in the South Caucasus and other areas of the world. The countries of the South Caucasus rank low on women’s participation in parliament compared to many other countries.New Policy Advice on Migration and Development in Georgia
Abortion rates in the South Caucasus among the highest in the world
Caucasus Barometer | A New Name for the CRRC's Data Initiative
Attitudes toward the West | Caucasus Analytical Digest
The Public's View of Constitutional Reform in Georgia
The CRRC Georgia Team
These are the CRRC Georgia team members who work hard on the numbers we usually present!Is the Caucasus in Europe or Asia? | Tim Straight at TEDxYerevan
Friends Are Hard To Come By: Friendship Divides by Gender in Azerbaijan
Overcoming Negative Stereotypes in the South Caucasus
Policy Attitudes towards Women in Azerbaijan: Is Equality Part of the Agenda?
Caucasus Data: Tolerance towards Others
Cuil for the Caucasus? A quick test!
Russian-Georgian Relations | Alex Rondeli on July 29
What do Russians think about the situation in Abkhazia and South Ossetia? -- Data Snapshot
Focus on non-oil tax policy as oil revenues predicted to decline
South Caucasus Data 2007 on Unemployment
McCain vs Obama: Caucasus preferences
World Economic Forum Gender Gap Index | a few surprises
History vs Public Policy
Snapshots on Attitudes towards Education
Financial Sector Snapshot - Armenia
A special issue of the Armenian Journal of Public Policy (published by AIPRG, with CRRC's Heghine Manasyan as one of the Editors) is devoted to Financial Sector Development. All the papers are engaging for non-specialists.Student Migration from the South Caucasus
Snapshot: Border Crossing Armenia-Georgia
How Many Tetri Are in a Lari? The Importance of Municipal Statistics for Good Governance
The government of Georgia has committed itself to collecting and publishing policy-relevant data in a timely manner under the Open Government Partnership. Yet while most ministries and state agencies are happy to provide national-level statistics, they often fail to break them down to the municipal level. Framing it in monetary terms, the current system means that officials do not know how many tetri are in a lari.Was the population informed about the constitutional reform in Georgia?
After 10 months of discussions, the parliament of Georgia adopted amendments to the constitution of the country on September 29th and overrode the president’s veto on October 13th, 2017. The most widely discussed amendments are about rules for electing the president, self-governance principles, the definition of marriage, the sale of agricultural land to foreigners, the minimum age of judges and the country’s foreign policy orientation. Because of the importance of the amendments, one would expect a high level of awareness among the population. However, despite the public meetings held and media coverage of the issue, according to the CRRC/NDI survey from June 2017, a majority of the population of Georgia was not aware of the constitutional reform process.Do people in Georgia see the government as a parent or as an employee?
Based on CRRC’s Caucasus Barometer survey data, this blog post describes how people in Georgia see the government, as a “parent” or as an “employee”, and how this differs by settlement type, gender, and education level.The Caucasus Barometer survey regularly asks people, “Which of the following statements do you agree with: “‘People are like children; the government should take care of them like a parent’ or ‘Government is like an employee; the people should be the bosses who control the government.’” Approximately half of the population of Georgia (52%) agreed in 2017 with the former statement and 40% with the latter. Responses to this question have fluctuated to some extent over time, but overall, attitudes are nearly equally split.
Pension reform is underway in Georgia, but only about half of the population is aware of it
On July 21, 2018 Georgian legislators approved an accumulative pension scheme, after years of discussion. As one of the requirements of the new law, employees with contracts who are under the age of 40 have to contribute 2% of their remuneration to the state-run pension fund, on a monthly basis. Although other employees are not legally required to do so, they may participate in the scheme voluntarily. This law is a first step in a larger reform of Georgia’s pension system. Opposition politicians have criticized the new law citing that it counters the country’s constitution as it introduces a new tax without a referendum. Several civil society groups also expressed criticism of the reform, questioning its legitimacy.Budget priorities are similar to people's spending priorities
Georgia’s state budget amounted to GEL 12.5 billion in 2018. The Ministry of Labor, Health and Social Affairs; Ministry of Regional Development and Infrastructure; and Ministry of Education and Science had the largest appropriations at 28.2% (GEL 3.528 billion), 14.5% (GEL 1.815 billion), and 9.5% (GEL 1.186 billion) of the budget, respectively. In the 2018 June CRRC/NDI survey, respondents were asked, “What are your top three priorities for spending, understanding it means cutting elsewhere?” Respondents were provided with a show card and allowed to name up to three answers. This blog post looks at whether responses match up with actual spending, and how priorities vary among different demographic groups.What were the greatest successes of Shevardnadze, the UNM, and Georgian Dream?
Each government of Georgia has had a wide range of successes; but how do the public see these successes from Shevardnadze’s time to the present?
When Eduard Shevardnadze’s government is mentioned in Georgia today, it tends to be connected with the dark times Georgia experienced in the 1990s. Yet, his government also saw the introduction of the Georgian Lari, resulting in a stable exchange rate. The United National Movement is credited with fighting petty corruption, and oversaw a period of relatively high economic growth, while at the same time failing to avoid the disastrous 2008 war with Russia. The Georgian Dream government too is seen as having had some success, for example, in reducing the prison population, from what was among the highest in the world. At the same time, incidents like the Gavrilov Nights and issues around election integrity are often cited as failures.
The greatest failures from Shevardnadze to Georgian Dream
While each Georgian government has had a range of successes, as described in another post published today, they have each had their own spectacular failures.
From Shevardnadze’s failure to establish state power outside Tbilisi, to the human rights abuses under the UNM and Gavrilov’s Nights under Georgian Dream, every government has had significant shortcomings.
While these are some of the most memorable, little research has been conducted on what the public thinks are the largest failings of each government. Data released on Tuesday from a CRRC Georgia survey conducted in partnership with the Levan Mikeladze Foundation and Carnegie Europe provides a picture of the public’s views of the largest successes and failures of government.